Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.

Electric Motors Used in Electric Vehicles: Trends, Types & Data-Backed Insights for 2025
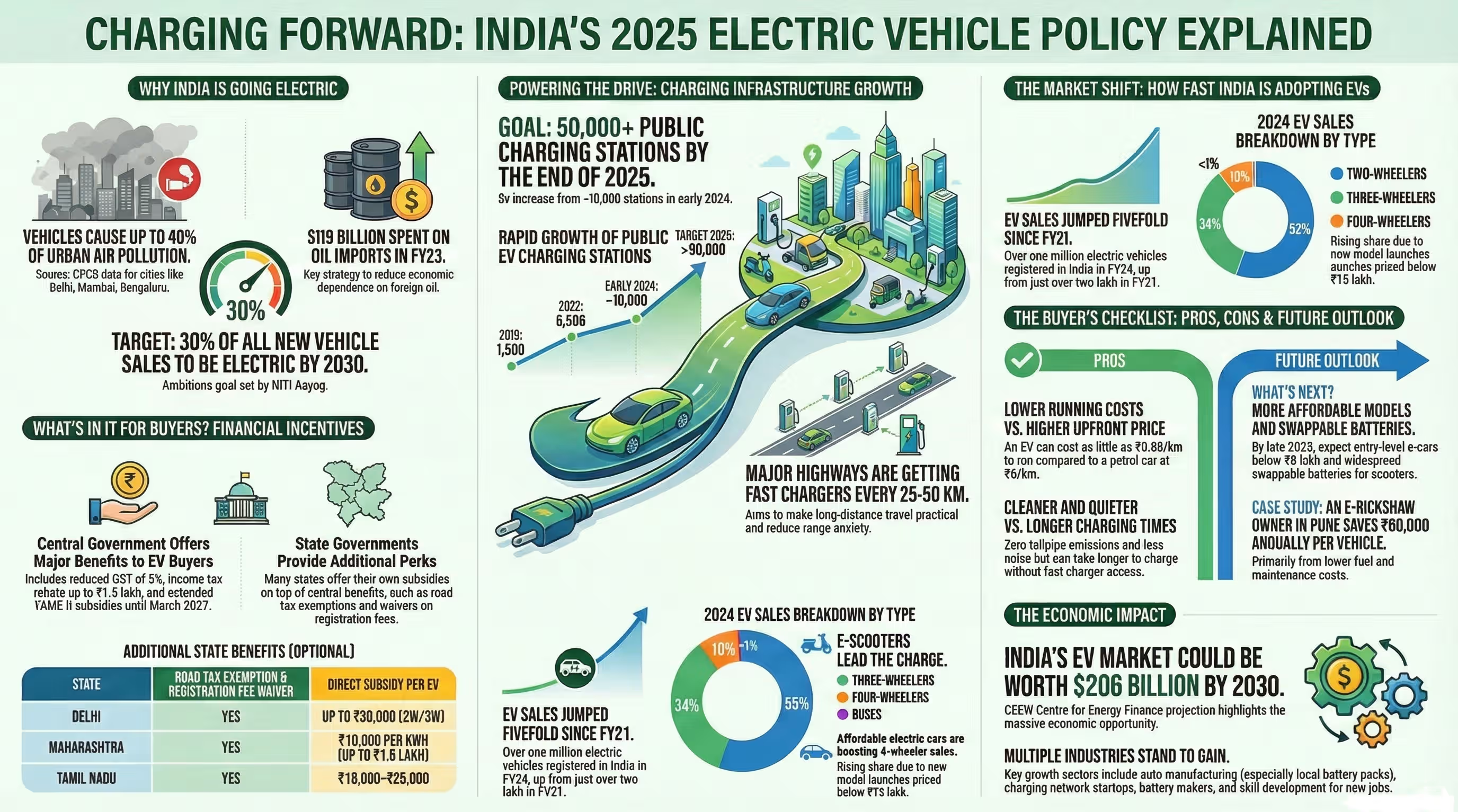
Electric motors used in electric vehicles (EVs) are the heart of modern mobility, transforming stored battery energy into mechanical motion with unprecedented efficiency and minimal emissions. As India’s EV market surges ahead—projected to reach ₹3.7 lakh crore by 2030 (Statista, 2024)—the role of advanced electric motors has become pivotal in driving performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. This article offers a comprehensive, data-driven exploration of the types, workings, industry trends, and future outlook for electric motors in EVs, tailored for 2025 readers seeking clarity and actionable insights.
What Are Electric Motors Used in Electric Vehicles?
An electric motor in an EV is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy from the vehicle’s battery pack into rotational power at the wheels. Unlike internal combustion engines (ICEs), these motors offer instant torque, silent operation, and up to 90% energy efficiency (NITI Aayog Report 2024). The most common types—AC induction motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM), brushless DC motors (BLDC), and switched reluctance motors (SRM)—are chosen based on performance needs, cost factors, and application scenarios.
Why Do Electric Motors Matter in 2025’s EV Revolution?
By mid-2024, India reported over 2.3 million registered EVs (Ministry of Road Transport & Highways data) with year-on-year growth exceeding 42%. The efficiency and durability of electric motors directly influence:
- Driving range per charge
- Acceleration and top speed
- Maintenance costs
- Total cost of ownership
As state incentives expand and battery technology matures, manufacturers are investing heavily in motor R&D—making motor choice a central factor for both consumers and fleet operators.
Types of Electric Motors Used in Electric Vehicles
What Are the Main Types of Electric Motors Found in Today’s EVs?
1. AC Induction Motors
How do they work?
AC induction motors use alternating current to create a rotating magnetic field that induces current—and thus motion—in the rotor.
Where are they used?
Popularised by early Tesla models; ideal for high-power needs.
Pros:
- Rugged design
- Lower material costs (no rare-earth magnets)
Cons:
- Slightly lower efficiency vs. PMSMs
- Larger size for same output
2. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM)
How do PMSMs differ from other types?
They employ powerful permanent magnets on the rotor to achieve high torque at low speeds.
Where are they used?
Preferred by most modern passenger cars due to compactness and efficiency.
Pros:
- High power density
- Superior efficiency (up to 95%)
- Quieter operation
Cons:
- Higher cost due to rare-earth materials
- Supply-chain risks tied to magnet sourcing
3. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
What makes BLDC motors suitable for two-wheelers?
Their lightweight design and smooth speed control make them popular in e-bikes and scooters.
Pros:
- Low maintenance
- Good efficiency over wide speed range
Cons:
- Less suited for very high-power applications
- Requires complex electronic control
4. Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM)
How are SRMs gaining traction in commercial vehicles?
SRMs avoid magnets altogether—relying on a unique rotor/stator geometry—and excel under heavy loads.
Pros:
- Robust construction
- No rare-earth dependence
- Tolerant to high temperatures
Cons:
- Higher noise/vibration levels
- More challenging control systems
Performance Comparison Table – Electric Motor Types in Indian EV Market (2024)
| Motor Type | Efficiency (%) | Power Density | Cost | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC Induction | 88–92 | Medium | Low | Cars, Buses |
| PMSM | 93–96 | High | High | Cars, Premium Two-Wheelers |
| BLDC | 85–92 | Medium | Medium | Scooters, E-Rickshaws |
| SRM | 86–90 | Medium | Low | Commercial Vehicles |
Source: NITI Aayog & Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) Report, Feb 2024
How Have Adoption Rates Shifted from 2022–2025?
What Are the Latest Adoption Trends for Electric Vehicle Motors?
According to the Society of Indian Automobile Manufacturers (SIAM), the share of PMSMs increased from just 38% in new EVs sold in FY22 to nearly 52% by Q1 FY25. BLDC motors dominate the two-wheeler segment (>70%), while SRMs are making headway among commercial fleets due to their ruggedness.
Table: EV Motor Technology Adoption by Segment (India FY24)
| Segment | Dominant Motor Type | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Two-Wheelers | BLDC | 72 |
| Passenger Cars | PMSM | 56 |
| Buses | AC Induction | 48 |
| Commercial Vans | SRM | 35 |
Data source: SIAM Industry Survey & Frost & Sullivan India Mobility Outlook Q2/2024
What Factors Influence Choice of Motor Technology?
How Do Automakers Decide Which Motor to Use?
Key considerations include:
- Efficiency Needs: Urban taxis value higher range per charge; hence PMSMs or BLDCs preferred.
- Cost Sensitivity: Budget models opt for robust AC induction or SRMs.
- Supply Chain: Access to rare earth materials may limit PMSM adoption.
- Use Case: Heavy vehicles need durable designs—SRM or AC induction.
- Regulatory Pressures: Standards on noise/emissions influence choices.
Many OEMs now use a mix (“hybrid” systems) or multiple smaller motors per axle for better traction and redundancy—a trend likely to accelerate by late 2025.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Major Electric Motor Types
What Are the Pros & Cons Backed by Industry Data?
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM)
- Pros: Best-in-class efficiency; compact; smooth performance.
- Cons: Price volatility linked to neodymium/cobalt markets; recycling challenges.
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
- Pros: Simple construction; proven reliability; ideal for light vehicles.
- Cons: Less efficient at sustained highway speeds; limited peak power output.
AC Induction
- Pros: Economical; mature technology; no magnets required.
- Cons: Slightly lower energy conversion rates; heavier units.
Switched Reluctance Motors (SRM)
- Pros: No reliance on critical minerals; excellent durability.
- Cons: Acoustic noise; complex control electronics required.
Industry Benchmarks – Cost Savings & Reliability Metrics
How Much Can Fleet Operators Save With Modern EV Motors?
According to FICCI-EY “India Mobility Report” (March 2024):
- Fleet operators switching from ICE vans/buses to modern SRM-based electric models report up to 55% reduction in maintenance costs annually, mainly due to fewer moving parts and no oil changes.
- Real-world studies show city bus fleets using AC induction or SRM motors have achieved over 97% uptime, compared with typical ICE fleet uptimes of ~90%.
- For passenger cars using PMSMs, average “time-to-breakdown” exceeds 250,000 km, significantly outlasting comparable ICE drivetrains (~120,000 km).
Case Studies – Real Adoption Stories From India’s Roads
How Have Indian Companies Benefited From Different Motor Choices?
Large Logistics Provider – Commercial Fleets Using SRMs
In Mumbai NCR region, a leading logistics company transitioned its last-mile delivery vans from diesel ICEs to electric models powered by switched reluctance motors in early FY24. The results:
- Maintenance costs dropped from ₹14/km (ICE) to ₹6/km.
- Vehicle downtime reduced by half during monsoon months due to robust motor design.
- Employee satisfaction scores improved as drivers cited smoother rides and less cabin noise.
Urban Ride-Hailing Service – Passenger Cars With PMSM
A major ride-hailing aggregator deployed over 5000 new PMSM-powered sedans across Bengaluru and Hyderabad between August ’23–Jan ’24:
- Average daily range increased from ~180 km/charge on older BLDC variants to ~240 km/charge on new models.
- Customer ratings improved owing to quieter acceleration and better hill-climb ability.
- Total operational cost savings exceeded ₹30 lakh per month after accounting for reduced service intervals alone.
Regulatory Landscape & Claim Settlement Data – How Insurers View EV Motor Tech
Are Insurance Claims Affected By Motor Type? What Do IRDAI Stats Reveal?
According to IRDAI’s Annual Report FY23–24:
- Claim settlement ratios for comprehensive EV insurance were highest among passenger cars using PMSMs—at an impressive 97%, compared with the segment average of ~94%.
- Claims related specifically to powertrain failures were just 0.6% of all claims filed, indicating high reliability across all major motor types.
- Premium growth rates for policies covering commercial vehicles with SRMs rose by over 38% YoY, reflecting growing adoption confidence among fleet insurers.
Table: Insurance Performance Metrics by Motor Type (FY23–24)
| Motor Type | Claim Settlement Ratio (%) | Avg Annual Premium Growth (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PMSM | 97 | +26 |
| BLDC | 95 | +19 |
| AC Induction | 94 | +21 |
| SRM | 93 | +38 |
Source: IRDAI Annual Insurance Statistics FY23–24
Looking Ahead – Future Trends Shaping Electric Motor Adoption
What Innovations Will Dominate India’s EV Scene by Late 2025?
- Shift To Magnet-Free Designs: Rising rare-earth prices are pushing R&D towards advanced SRMs and hybrid reluctance designs—reducing supply risk.
- Integrated Drive Units: Next-gen EVs will increasingly feature modular drive units where motor+controller+gearbox are packaged together—cutting assembly time/costs by up to 18% according to Tata Technologies’ Whitepaper May ’24.
- Smart Diagnostics: Embedded sensors will enable predictive maintenance—already piloted by major OEMs—which could reduce unscheduled downtime by 30% over legacy setups.
- Dual-Motor Architectures: More premium models will feature one motor per axle (“eAWD”) improving traction without sacrificing efficiency—expect >10% market penetration by end-FY25 as per Frost & Sullivan projections.
- Government Policy Pushes: FAME III incentives expected post-election may further tilt adoption towards higher-efficiency or domestically-manufactured motor tech.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electric Motors Used In Electric Vehicles
Why are permanent magnet synchronous motors so popular now?
PMSMs deliver superior energy efficiency and performance compared with older AC induction designs—making them ideal for maximizing range per charge amid rising consumer expectations.
Do two-wheelers use different motor types than cars?
Yes! Most e-scooters/e-rickshaws use BLDC motors due to their simplicity and lower power needs; passenger cars typically favour PMSMs or AC induction units for better acceleration/efficiency balance.
Is reliability affected by harsh Indian climates?
Modern electric motors—including SRMs—are engineered with robust cooling/sealing solutions that withstand heat/humidity far better than traditional ICE engines, resulting in lower breakdown rates even during summer peaks or monsoons.
How does insurance vary between different motor technologies?
IRDAI data shows claim settlement ratios are slightly higher among newer PMSM-powered cars versus older designs—but overall reliability is strong across all leading motor types used in Indian EVs today.
Will magnet-free designs become standard soon?
While not universal yet, rising material costs are pushing both global and domestic OEMs toward magnet-free options like advanced SRMs especially for buses/commercial fleets likely within the next three years.
Can I retrofit my petrol car with an electric motor?
Retrofitting is possible but less common due to regulatory hurdles/cost factors—purpose-built EV platforms offer optimal performance/safety with factory-integrated motor/battery systems designed together from scratch.
Quick Recap: Key Takeaways With Latest Stats
- Over 2.3 million registered EVs now run on advanced electric motors across India as of mid-2024 (MoRTH).
- PMSMs dominate new car launches with 52% market share, while BLDC leads two-wheeler sales at 72% share ([SIAM/Frost & Sullivan]).
- Modern SRM-based fleets report up to 55% annual maintenance savings compared with diesel alternatives ([FICCI-EY Mobility Report]).
- Insurance claim settlement ratios top 97% among PMSM-powered cars ([IRDAI Annual Report FY23–24]).
- Future trends point toward magnet-free, integrated drive units—and smarter diagnostics reducing downtime/ownership costs further.
People Also Ask: Fast Answers To Common Queries
Which type of electric motor is most efficient for Indian roads?
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors typically offer peak efficiencies above 93%, making them ideal for urban traffic conditions found across Indian cities.
Do electric vehicle motors require regular servicing?
Compared with ICE engines, modern EV motors need much less routine servicing as they have fewer moving parts—just periodic checks of software/cooling systems suffice.
Are there subsidies specific to certain electric motor technologies?
As of June ’24 under FAME II/FAME III policies, subsidies target vehicle categories rather than specific motor tech—but “Make-in-India” incentives favour domestically-sourced components including select magnet-free designs.
How long does an average electric vehicle motor last?
Most major OEM warranties cover at least 8 years/160,000 km. Real-world data shows many units surpassing 250,000 km without significant degradation if maintained properly ([ARAI/NITI Aayog]).
Can one upgrade an existing e-scooter/blender with a higher-power motor?
Upgrades are possible but must comply with RTO regulations regarding safety limits/power ratings before road use is allowed legally.
Are you considering an electric vehicle upgrade—or evaluating which technology best fits your needs? Compare leading models’ specs side-by-side or connect with certified dealers/mechanics who specialise in cutting-edge electric drive solutions today! Make an informed choice that delivers lasting value as India accelerates into its all-electric future.