Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.
Is Diesel Car to EV Conversion Legal in India - Rules, Cost & RTO Approval Explained
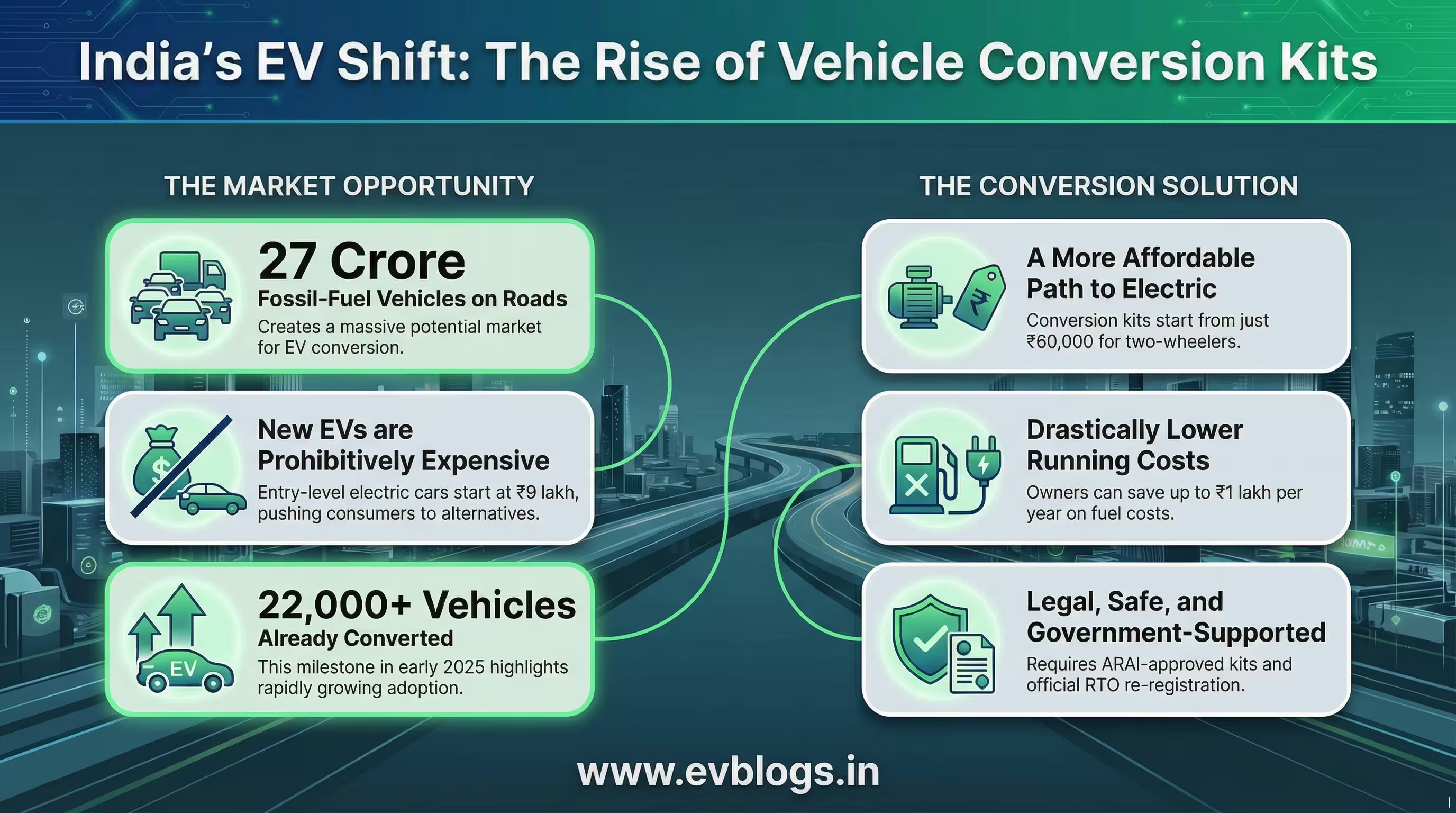
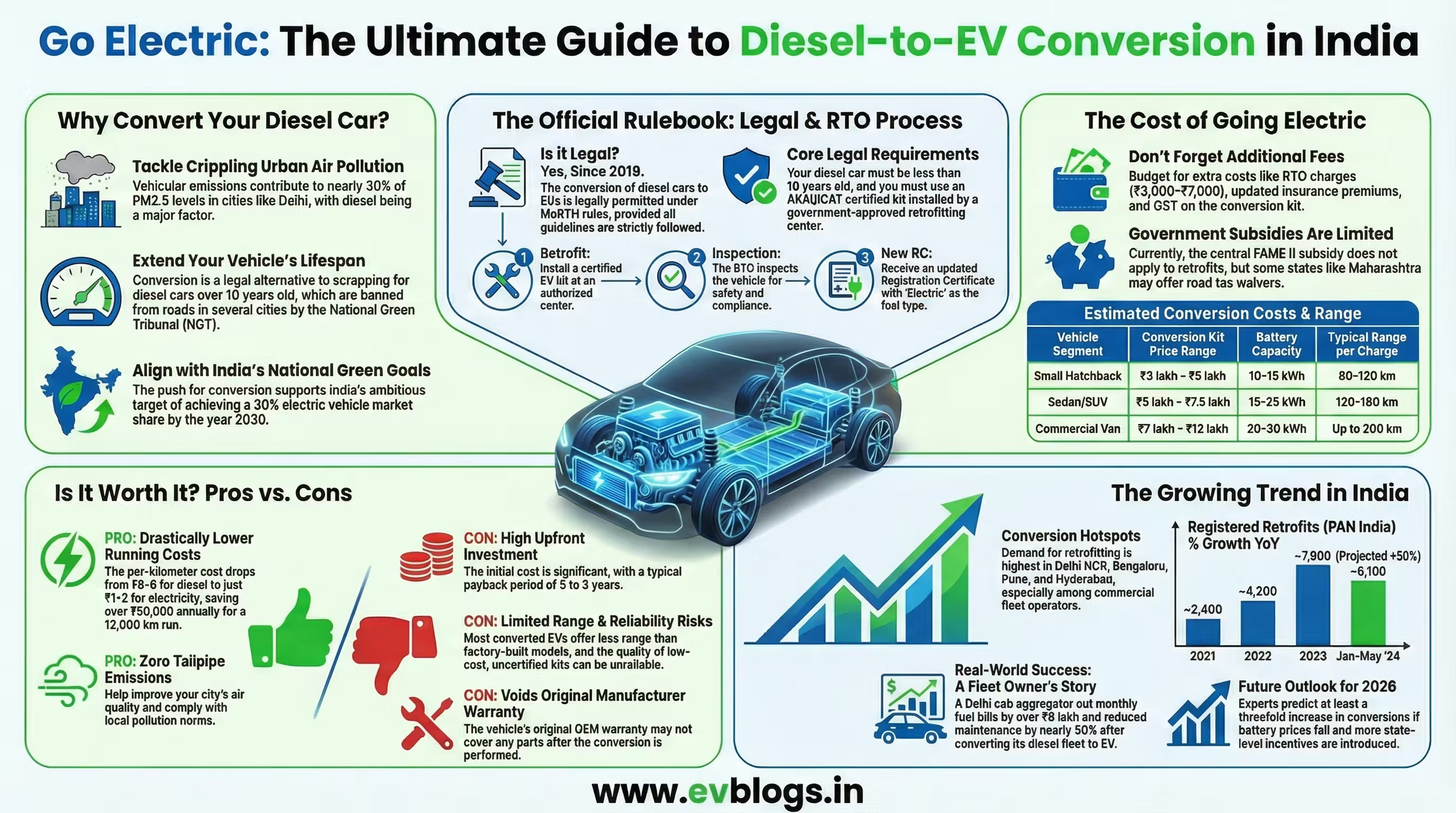
Yes, diesel car to EV conversion is legal in India since 2019, but only if you follow strict rules set by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) and get mandatory RTO approval. In 2024, the government updated guidelines for retrofitting old diesel vehicles with electric kits, especially as pollution laws get stricter in major cities. If you own a diesel car and want to switch to electric for cheaper running costs and a greener drive, it is possible—provided you use certified kits and comply with registration rules. Read on for all the facts, latest costs, legal steps, and what to expect in 2025.
Why Is Diesel Car to EV Conversion Important in India?
India faces growing air pollution in urban areas. According to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), vehicular emissions account for nearly 30% of PM2.5 levels in cities like Delhi and Mumbai (CPCB Annual Report 2023). Diesel vehicles are a major contributor due to higher particulate emissions.
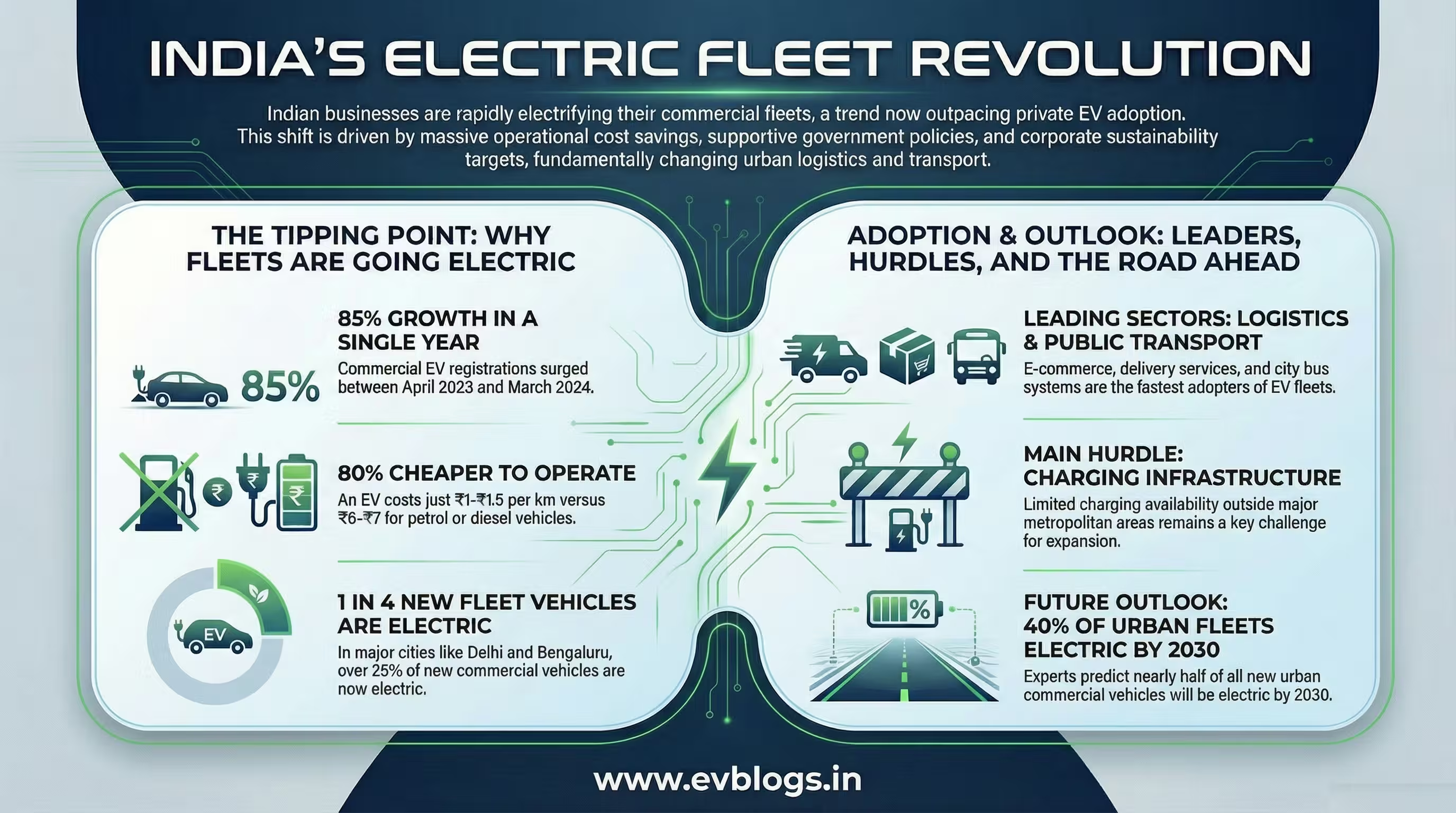
With the National Green Tribunal (NGT) banning 10-year-old diesel cars in several cities, lakhs of owners are now looking at electric conversion as an alternative to scrapping their vehicles. The push aligns with India’s target of having 30% electric vehicle market share by 2030 (NITI Aayog/World Economic Forum report).
What Are the Official Rules for Diesel Car to EV Conversion?
What does the law say about converting diesel cars?
As per MoRTH Notification No. GSR 167(E) dated 8 March 2018 (amended up to 2024), converting diesel or petrol vehicles into electric ones is permitted if:
- The base vehicle is not more than 10 years old (diesel) or 15 years old (petrol).
- Only government-approved retrofitting centres can install conversion kits.
- Kits must have Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) or ICAT certification.
- Post-conversion inspection and fresh registration at the RTO is compulsory.
How does RTO approval work?
- Retrofitting: Get your car fitted with a certified EV kit at an authorised centre.
- Inspection: The RTO inspects the converted vehicle for safety and compliance.
- New RC: After passing inspection, you receive an updated Registration Certificate reflecting ‘Electric’ as fuel type.
Failing to follow these steps can lead to fines or de-registration under section 52 of the Motor Vehicles Act.
How Much Does Diesel Car to EV Conversion Cost in India?
What are typical costs involved in conversion?
The cost depends on your car model, battery size, and kit quality.
| Vehicle Segment | Conversion Kit Price Range | Battery Capacity | Typical Range per Charge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small hatchback | ₹3 lakh–₹5 lakh | 10–15 kWh | 80–120 km |
| Sedan/SUV | ₹5 lakh–₹7.5 lakh | 15–25 kWh | 120–180 km |
| Commercial van | ₹7 lakh–₹12 lakh | 20–30 kWh | Up to 200 km |
Source: FADA-EV Retrofitting Survey Report Q1 2024
Additional fees include RTO charges (₹3,000–₹7,000), insurance premium update (varies), and GST on kits.
Are there any government subsidies?
Currently, FAME II subsidies apply only to new EVs—not retrofits. However, some state governments like Maharashtra offer waivers on road tax for converted vehicles.
Is It Worth Converting Your Diesel Car? Pros & Cons
What are the benefits and drawbacks?
Pros
- Lower running cost: Electricity cost per km drops from ₹6–8 (diesel) to ₹1–2.
- No fuel price worries: Save over ₹50k annually if driving >12,000 km/year.
- Cleaner city air: Zero tailpipe emissions; helps meet local air quality norms.
- Extended vehicle life: Avoids scrapping after NGT bans; good for sentimental or classic cars.
Cons
- High upfront investment: Payback period is typically 3–5 years.
- Limited range: Most conversions offer less range than factory-built EVs.
- Kit quality varies: Some low-cost kits have reliability issues; always choose certified installers.
- Voids original warranty: OEM support may not cover converted vehicles.
How Many Indians Have Converted Their Cars? Adoption Rates & Trends
According to a June 2024 FADA report:
| Year | Registered Retrofits (PAN India) | % Growth YoY |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ~2,400 | — |
| 2022 | ~4,200 | +75% |
| 2023 | ~7,800 | +86% |
| Jan-May ‘24 | ~6,100 | Projected +50% |
Retrofit demand is highest in Delhi NCR, Bengaluru, Pune, Hyderabad—especially among fleet operators seeking lower TCO (total cost of ownership).
Real-Life Example: A Fleet Owner’s Experience
A popular cab aggregator in Delhi converted its fleet of older diesel sedans into electric using ARAI-certified kits between April-November 2023. Within eight months:
- Monthly fuel bills dropped by over ₹9 lakh across the fleet
- Maintenance issues reduced by nearly half
- Drivers reported quieter rides and fewer breakdowns
However, initial teething issues included longer downtime during conversion and some compatibility problems with older models—solved after switching suppliers.
Future Outlook: Will More Indians Convert Diesel Cars by 2026?
With rising fuel prices and stricter emission laws expected by mid-decade—plus growing awareness about climate change—demand for legal diesel-to-EV conversions should keep rising steadily through 2026. Industry experts predict at least a threefold increase from today’s numbers if battery prices fall below $100/kWh and more state incentives roll out.
The government may also expand policy support as India targets net zero by 2070 (PIB Report). Watch out for new rules under Bharat Mobility standards due late next year.
Quick Recap & Key Takeaways
- Diesel car to EV conversion is legal if done with certified kits and RTO approval.
- Costs range from ₹3 lakh–₹12 lakh depending on vehicle type and battery size.
- Running costs drop sharply after conversion; payback period is around three years.
- Retrofit adoption grew nearly threefold between 2021–24; strongest uptake seen among commercial fleets.
- Always check MoRTH/ARAI/State Transport websites (MoRTH Circulars) for updates before starting conversion.
People Also Ask
Q1. Can I convert my old diesel car into an electric vehicle legally? Yes—but only if your car is under ten years old and you use an approved conversion kit at a certified centre with proper RTO paperwork.
Q2. Is there any subsidy for converting diesel cars into electric? Currently no central subsidy exists for conversions; some states may offer tax waivers or registration benefits.
Q3. How long does it take to complete an EV retrofit? Most conversions take two–four weeks including installation and approvals.
Q4. Will my insurance policy remain valid after converting my car? You must inform your insurer about the change; expect a revised premium based on new specifications.
Q5. Can all types of diesel vehicles be converted? Most standard passenger cars can be converted if parts are available; luxury/high-end cars may face technical challenges.
Q6. Where can I find official guidelines about retrofitting? Visit MoRTH Official Portal, ARAI (araiindia.com), or your state transport department website for detailed circulars.
Ready for a greener drive? If you want to convert your diesel car into an electric one legally in India—start by checking government guidelines above or contact a certified retrofit centre near you today! Save money every kilometre while helping clean up our cities’ air.