Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.

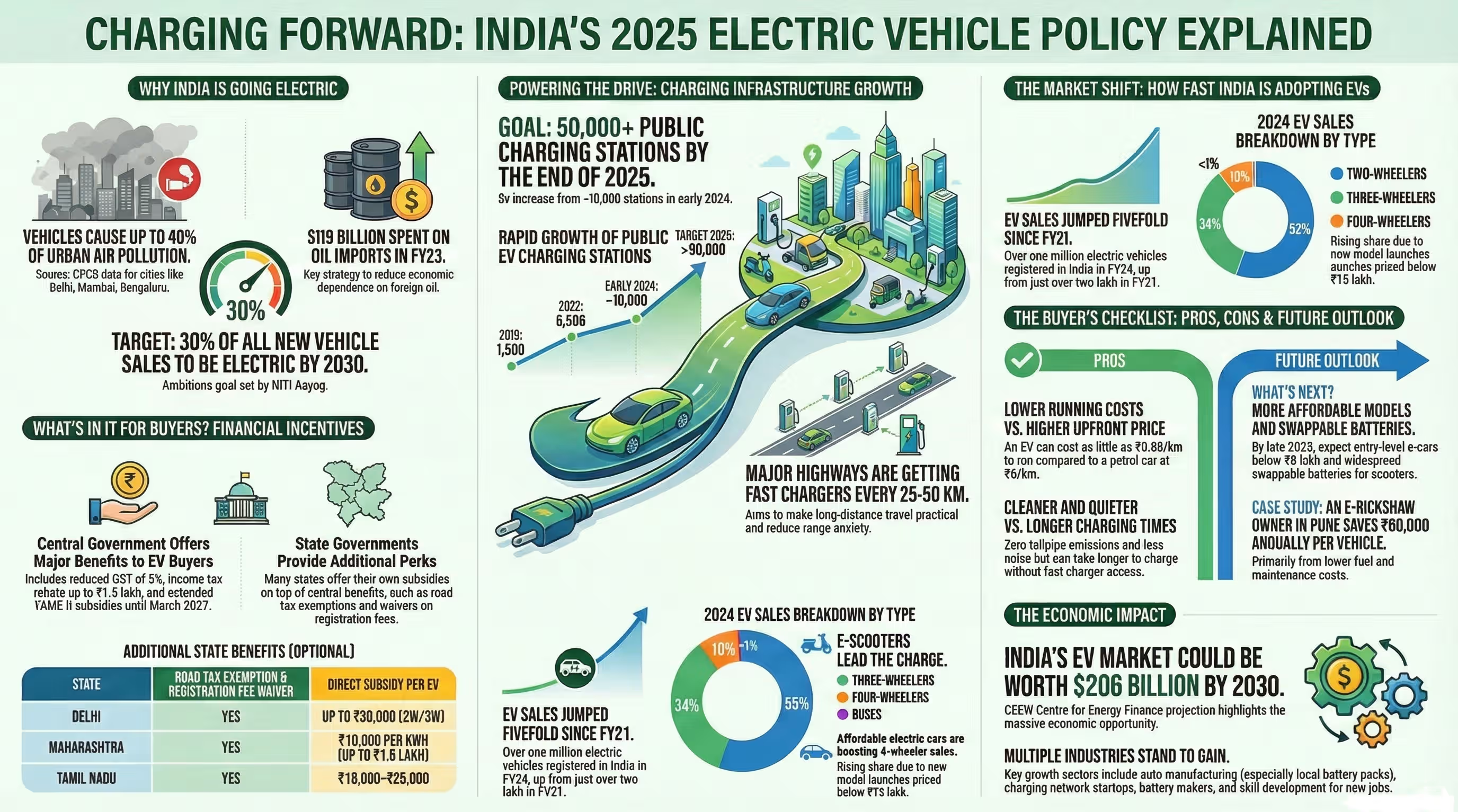
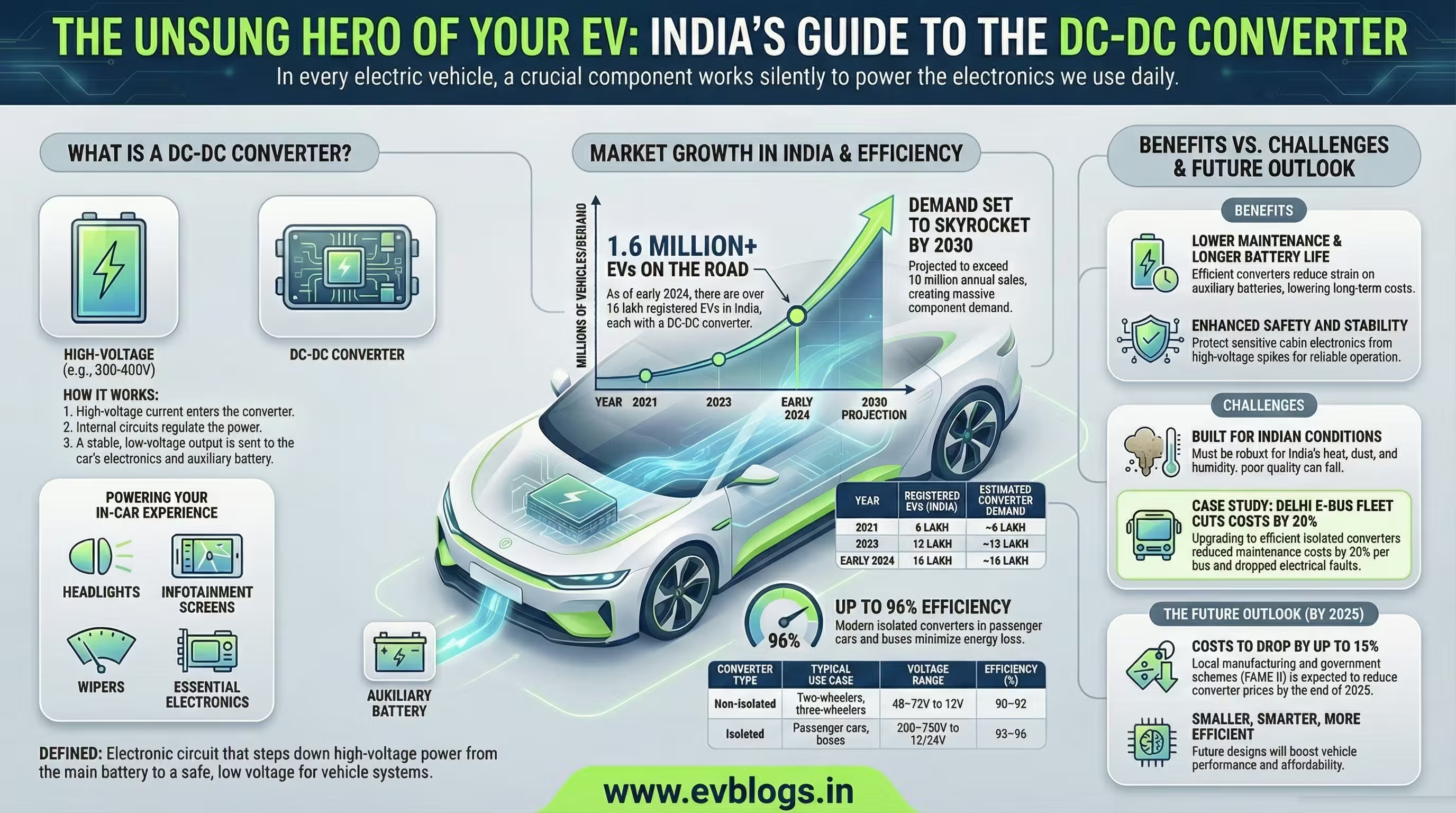
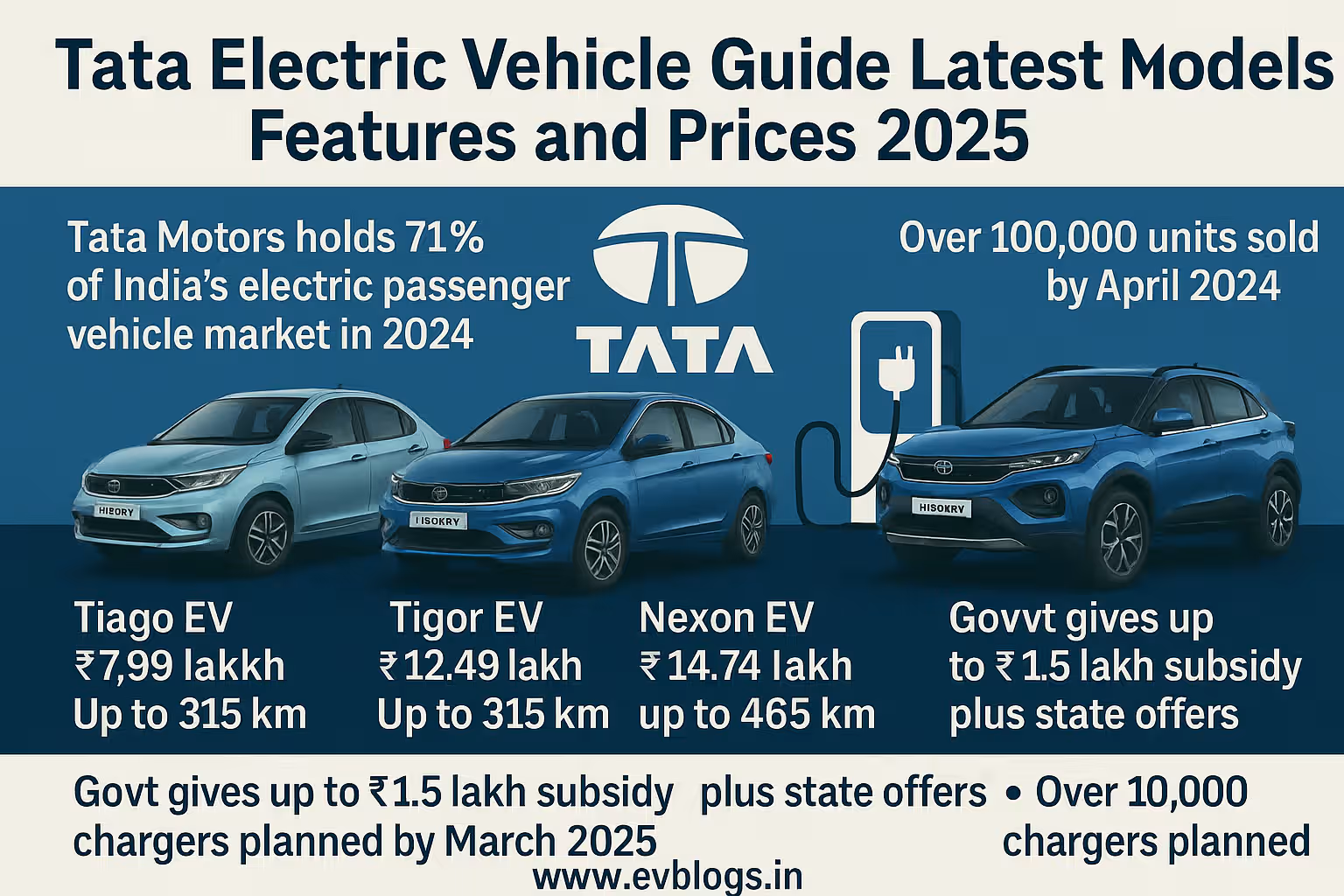
NEW DELHI, Dec 12 — As India accelerates its transition towards electric mobility, the nation’s demand for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is projected to rise exponentially, reaching an estimated 256.3 gigawatt-hours (GWh) by 2032, according to a recent report. This surge in demand reflects India’s ambition to become a leading market for clean transportation and renewable energy solutions. Below, we explore the key factors driving this growth and its implications for the country’s automotive and energy sectors.
1. Unprecedented Growth in EV Adoption
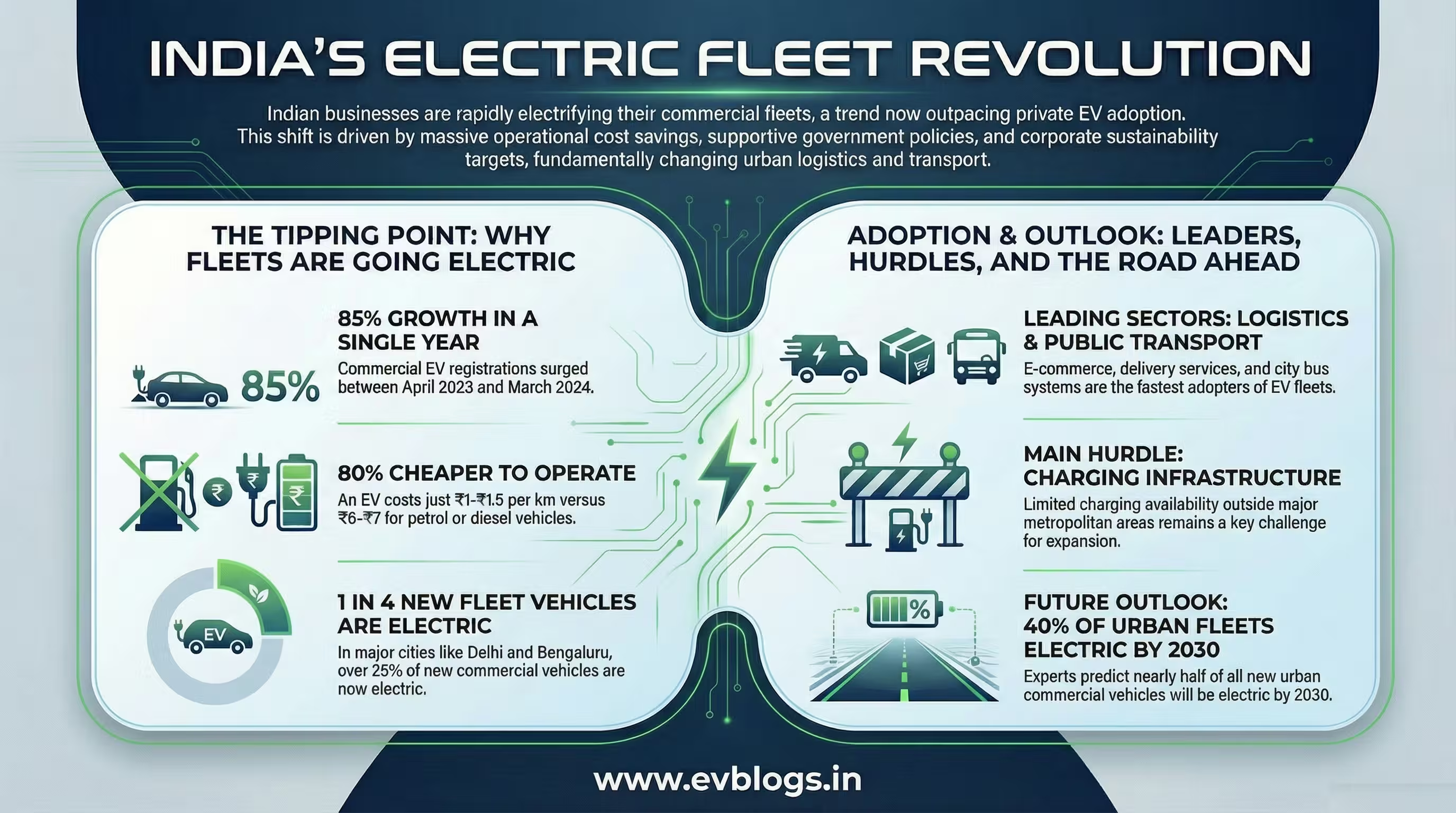
India’s electric vehicle market has witnessed remarkable growth in recent years, especially in the two-wheeler and three-wheeler segments. Sales of electric vehicles are expected to cross 10 million units annually by 2030.
“The growing consumer preference for cleaner mobility options is a major catalyst behind the rising demand for EV batteries in India.”
Government incentives, stricter emission norms, and rising environmental awareness are further accelerating this trend, setting the stage for an exponential increase in battery demand over the next decade.
2. Government Policies Fueling Battery Demand
The Indian government has introduced several policy measures, such as the FAME II scheme (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) and the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) battery storage. These initiatives aim to:
- Boost local manufacturing of batteries,
- Reduce import dependency,
- Promote research and development in battery technologies.
“Under FAME II, the government has allocated ₹10,000 crore to encourage EV adoption and infrastructure development.”
These policies are expected to play a pivotal role in meeting the projected demand of 256.3 GWh by 2032.
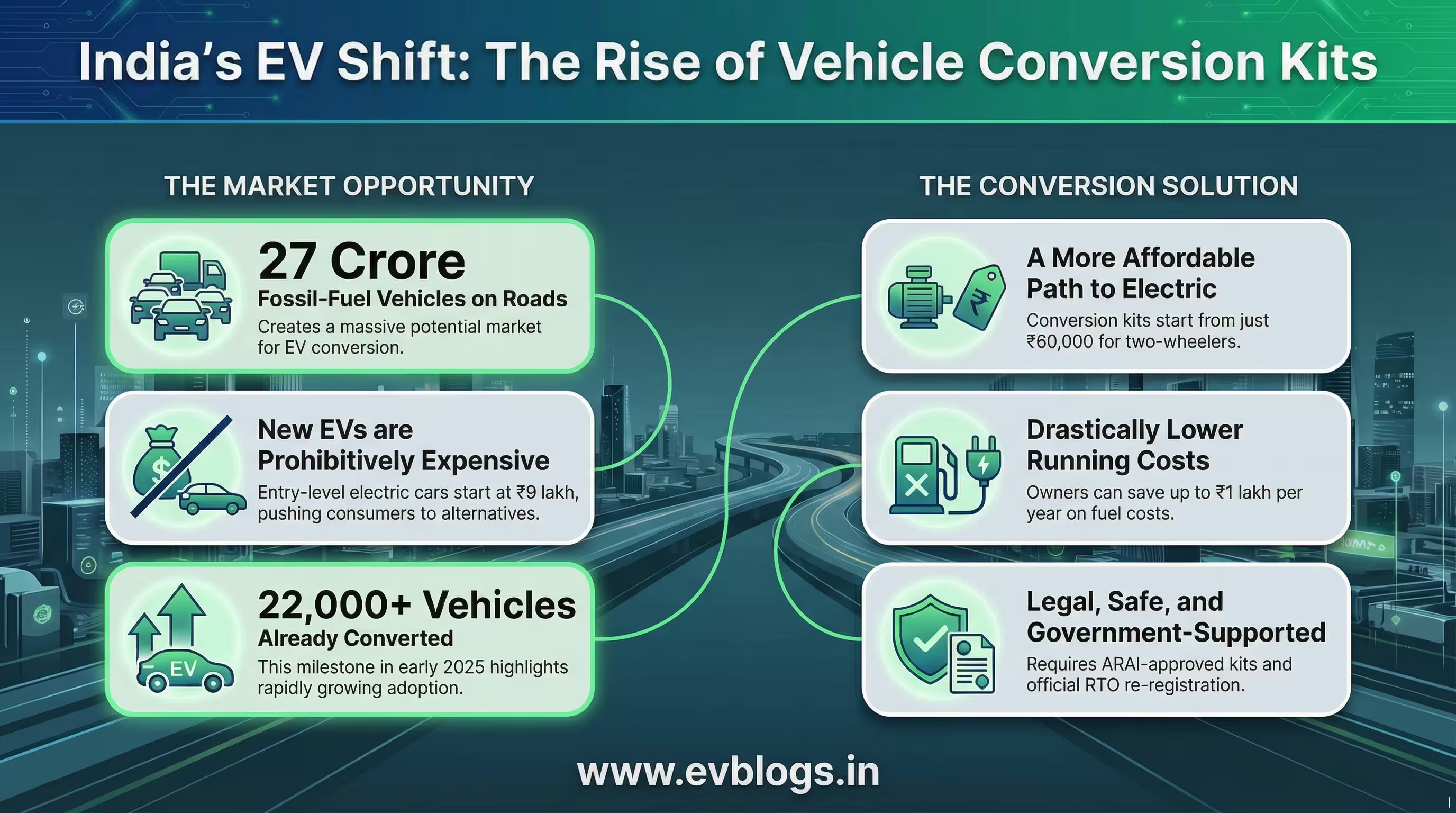
3. Expansion of Domestic Battery Manufacturing
India is rapidly emerging as a hub for EV battery production. Several domestic and international companies have announced plans to set up gigafactories, with capacities ranging from 5 to 20 GWh each.
Reliance Industries, Ola Electric, and Tata Group are among the major players investing in large-scale battery manufacturing facilities.
This expansion not only supports the local EV ecosystem but also positions India as a potential exporter of advanced battery technologies in the future.
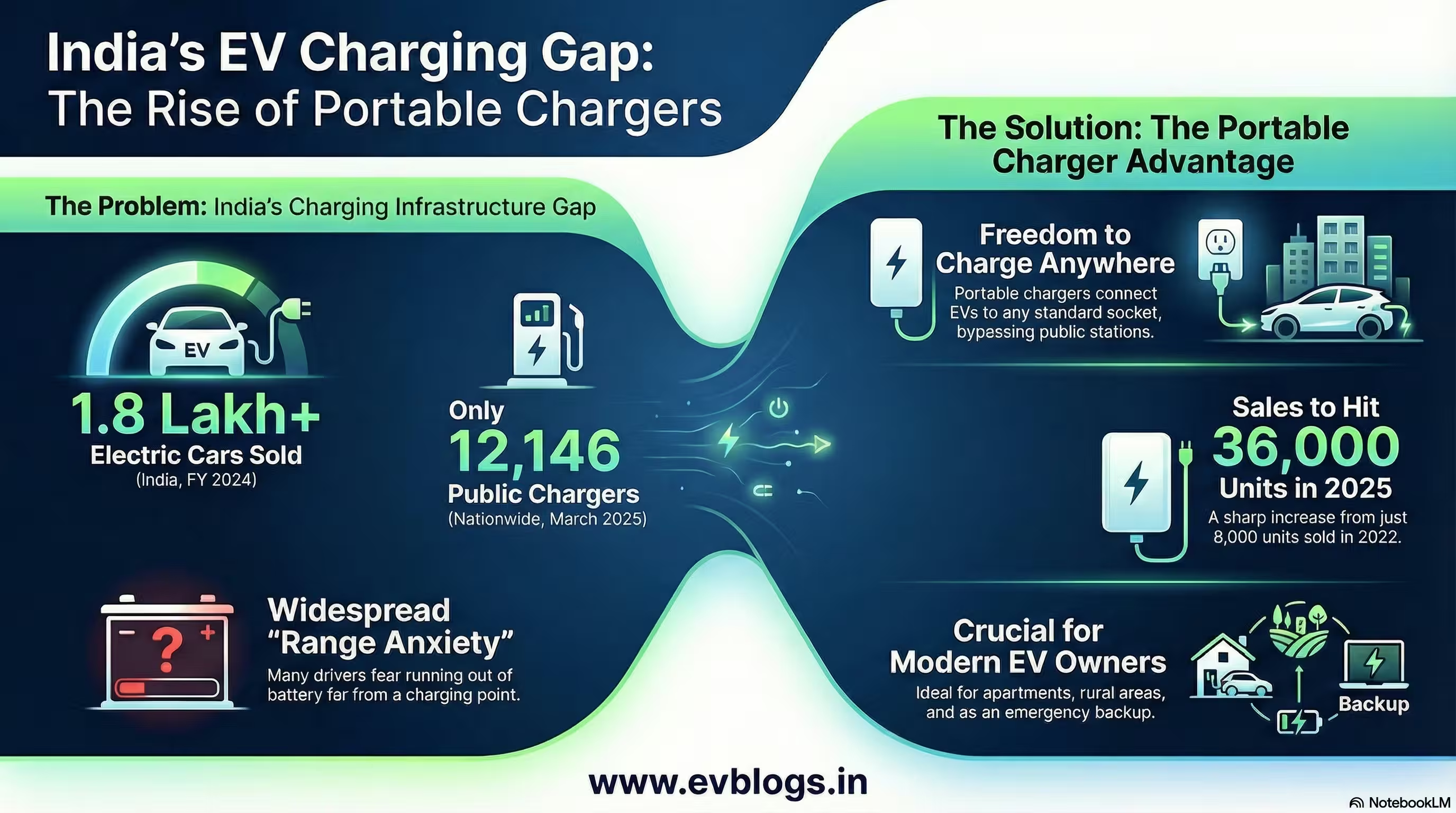
4. Investment in Charging Infrastructure
The availability and accessibility of charging stations are crucial for large-scale EV adoption. The government and private sector are investing heavily in nationwide charging infrastructure, aiming to install over 70,000 public charging stations by 2025.
“Robust charging infrastructure is essential to support the anticipated surge in battery-operated vehicles.”
This development will further stimulate demand for batteries and associated energy storage solutions.
5. Technological Advancements and Innovation
Continuous innovation in battery chemistry and manufacturing is leading to higher energy densities, faster charging times, and longer life cycles. Indian research institutions and startups are actively engaged in developing solid-state batteries, lithium-sulphur, and sodium-ion technologies.
Advanced battery technologies are expected to reduce costs by up to 30% and improve vehicle range significantly.
Such advancements are critical for sustaining growth and ensuring India’s competitiveness in the global EV market.
6. Environmental and Economic Benefits
The shift to electric mobility and the corresponding surge in battery demand are expected to deliver substantial environmental and economic benefits:
- Reduction in air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions,
- Decreased reliance on imported oil,
- Creation of new jobs in manufacturing, research, and services.
“By 2032, India could cut its annual CO₂ emissions by millions of tonnes through widespread EV adoption.”
These benefits reinforce the nation’s commitment to sustainable development and climate goals.
7. Challenges Ahead
Despite the optimistic outlook, several challenges remain:
- Dependence on raw material imports like lithium and cobalt,
- Need for effective battery recycling and waste management systems,
- High upfront costs and limited consumer awareness in semi-urban and rural areas.
“Addressing these challenges will be crucial to realising the full potential of India’s EV battery market.”
As India moves steadily towards a greener future, the projected surge in EV battery demand reflects both the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead. With continued policy support, investments in technology, and a focus on sustainability, India is well-positioned to become a global leader in electric mobility and battery manufacturing by 2032.
Sources
Original Source
google.com - Read original
Official Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): IPCC opens registration of experts to review the first draft of the Methodology Report on Inventories for Short-lived Climate Forcers
Quotes
- Publishing Domain: google.com
- Published Date: 2025-12-12T13:36:54+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMi3AFBVV95cUxQUTVzc0NDVUhEQ0g3cEFRd0ZwZ1pZU… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 10 / 100 — The summary is almost identical to the article title and does not provide any additional or unique information beyond what is already stated in the headline.
- Helpfulness: 20 / 100 — The summary conveys the main data point (India’s EV battery demand reaching 256.3 GWh by 2032), but lacks context, explanation, or supporting details that would help a reader understand the significance or implications of the report.