Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.
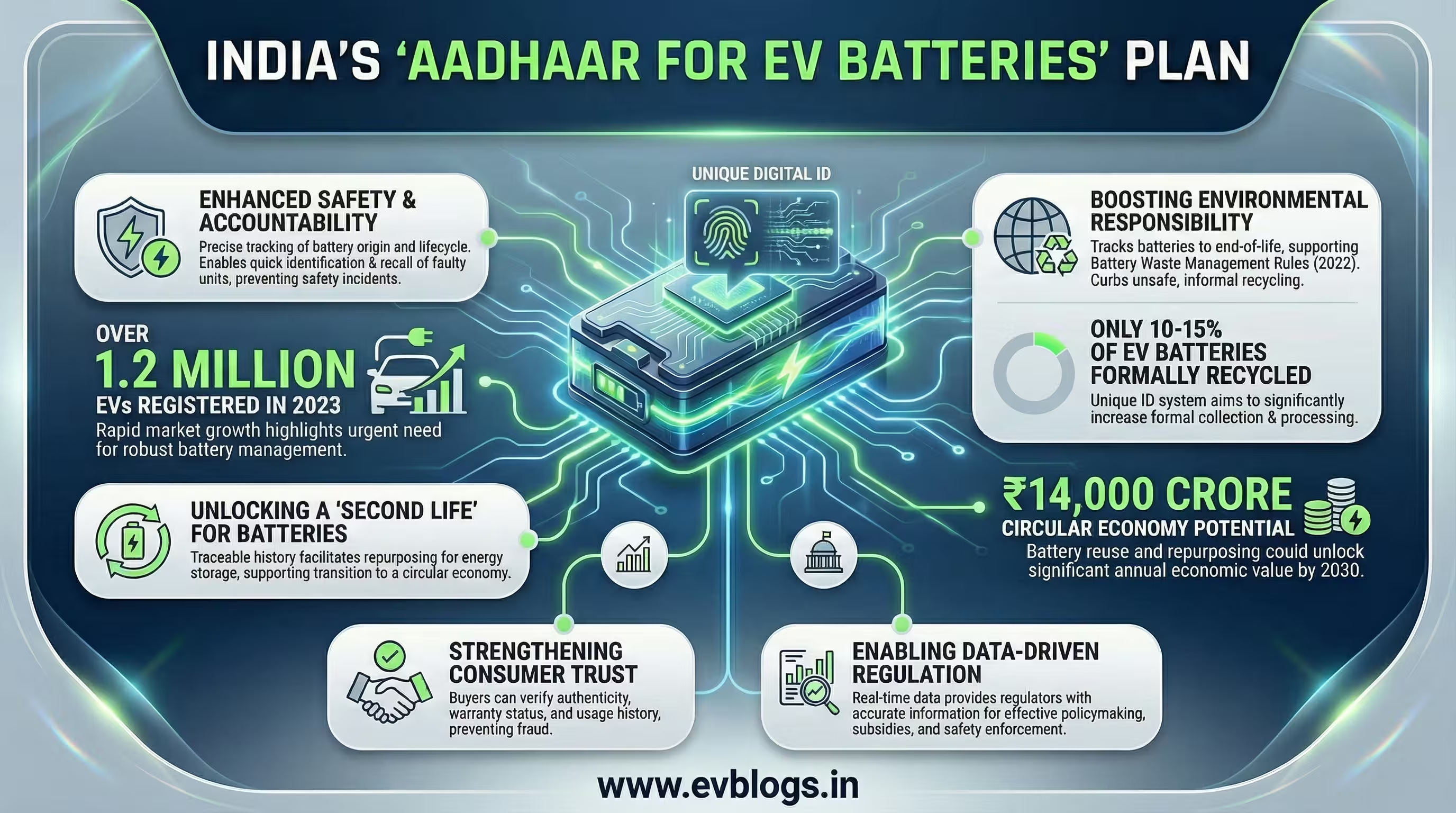
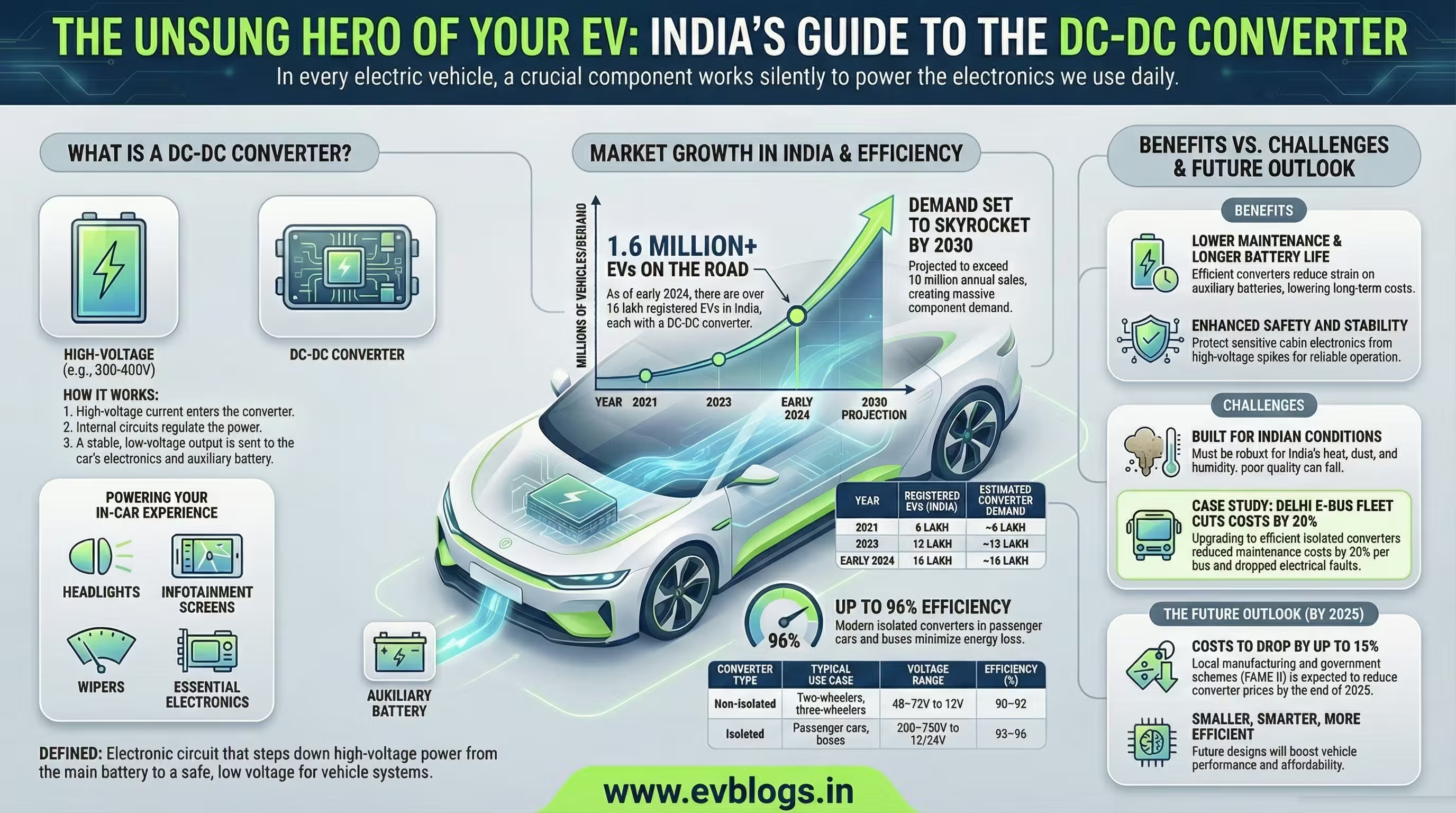
NEW DELHI, Jan 3 — In a significant move to strengthen the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has proposed introducing a unique identification number for each EV battery, similar to Aadhaar. This initiative aims to enhance traceability, improve safety standards, and facilitate responsible battery disposal across India. Here are the key aspects of the proposal:
1. Unique Identification Number for Every EV Battery
The ministry’s proposal calls for assigning a distinct, tamper-proof identification number to every EV battery sold in India. This number would be digitally linked to the battery’s lifecycle, allowing for real-time tracking from manufacturing to end-of-life.
“Over 1.2 million electric vehicles were registered in India in 2023, underlining the need for robust battery management systems.”
This system is expected to reduce instances of battery theft, illegal recycling, and unauthorised modifications, thereby promoting overall safety and transparency.
2. Enhanced Traceability and Accountability
With a unique ID, stakeholders—including manufacturers, dealers, and recycling agencies—will be able to track the movement and condition of each battery throughout its usage. This traceability will help authorities monitor battery health, identify faulty units, and ensure timely recalls if safety issues emerge.
“Traceability is crucial for investigating safety incidents such as battery fires, which have raised concerns in Indian cities.”
3. Boosting Battery Recycling and Environmental Responsibility
Battery disposal poses a significant environmental challenge in India. The proposed system will make it easier to track batteries reaching end-of-life, enabling efficient collection and recycling. This aligns with the government’s Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022, which mandate environmentally sound disposal.
“Only 10-15% of used EV batteries in India are currently recycled through formal channels.”
An Aadhaar-like tracking mechanism is expected to curb informal and unsafe recycling practices, reducing ecological risks.
4. Supporting Second-Life Applications and Circular Economy
Unique identification numbers will also facilitate the repurposing of used EV batteries for secondary applications, such as energy storage systems in rural or off-grid areas. By verifying the history and condition of each battery, companies can safely give them a ‘second life’, supporting India’s transition towards a circular economy.
“The circular economy approach could unlock up to ₹14,000 crore in annual economic value by 2030 through battery reuse.”
5. Strengthening Consumer Safety and Confidence
For end-users, the system promises greater transparency regarding battery specifications, warranty status, and safety recalls. Consumers will be able to verify whether a battery is genuine and trace its usage history—helping to prevent fraud and boosting confidence in EV adoption.
“Consumer trust is key to accelerating EV adoption in India, which currently stands at around 2.5% of total vehicle sales.”
6. Facilitating Policy Implementation and Data-Driven Regulation
The unique ID system will provide regulators with accurate, real-time data on battery usage, performance, and disposal. This will support more effective policymaking, targeted subsidies, and enforcement of safety and environmental norms.
“Data-driven regulation can address gaps in the rapidly growing EV market, ensuring sustainable growth and compliance.”
The proposal for an Aadhaar-like unique identification number for EV batteries marks a forward-looking step in India’s journey towards sustainable mobility. By enhancing traceability, safety, and environmental responsibility, the initiative has the potential to accelerate EV adoption while addressing critical challenges in battery management. Stakeholders across the EV ecosystem will be closely watching the next steps as the policy develops.
Certainly! Here’s an additional detailed numbered point about the proposal for an Aadhaar-like number for EV battery traceability:
- Enhanced Safety and Quality Assurance:
By assigning a unique identification number—akin to Aadhaar—to each electric vehicle (EV) battery, the transport ministry aims to significantly improve safety and quality control across the industry. This traceability mechanism will enable authorities to precisely track the origin, manufacturing details, and lifecycle of every battery. In the event of defects, recalls, or safety incidents (such as fires or malfunctions), regulators and manufacturers can quickly identify affected units, pinpoint the root cause, and initiate targeted corrective measures. This system not only enhances consumer safety but also compels manufacturers to maintain higher quality standards, as each battery’s history will be easily accessible and auditable throughout its operational life.
Let me know if you need more points or further details!
Sources
Original Source
google.com - Read original
Official Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): IPCC opens registration of experts to review the first draft of the Methodology Report on Inventories for Short-lived Climate Forcers
Quotes
- Publishing Domain: google.com
- Published Date: 2026-01-03T16:06:10+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMi2wFBVV95cUxOckl0ekpmbEVKSVpKNThzejRiRjBvW… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 65 / 100 — The idea of assigning an Aadhaar-like unique identification number for EV battery traceability is moderately original. While the concept of unique IDs for traceability is not new, its application specifically to EV batteries in India is a novel regulatory proposal.
- Helpfulness: 80 / 100 — The summary is helpful as it clearly states the main proposal from the Transport Ministry, which is relevant for stakeholders in the EV sector. However, it lacks details about implementation, potential benefits, and challenges, which would make it more informative.