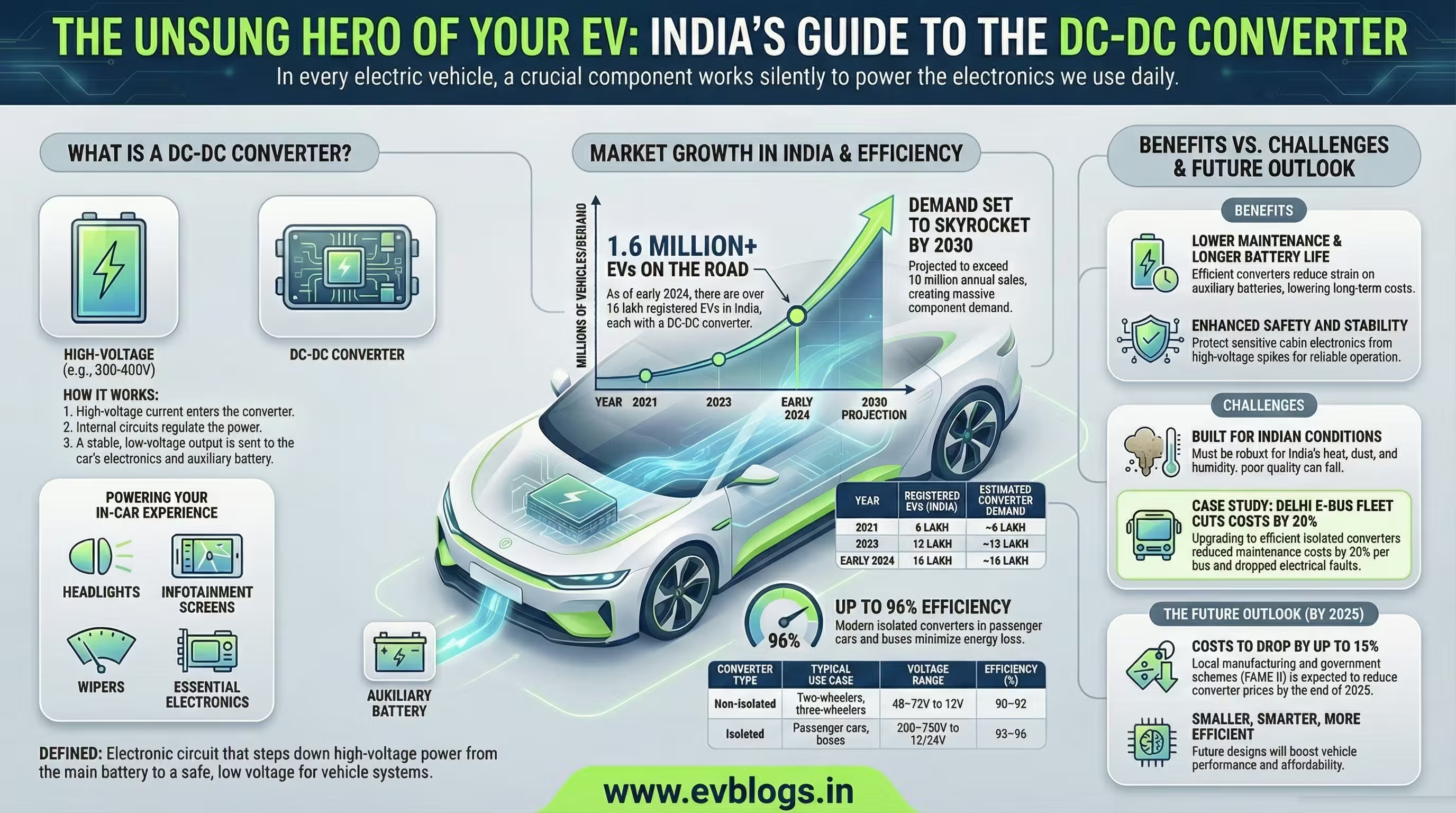
Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.
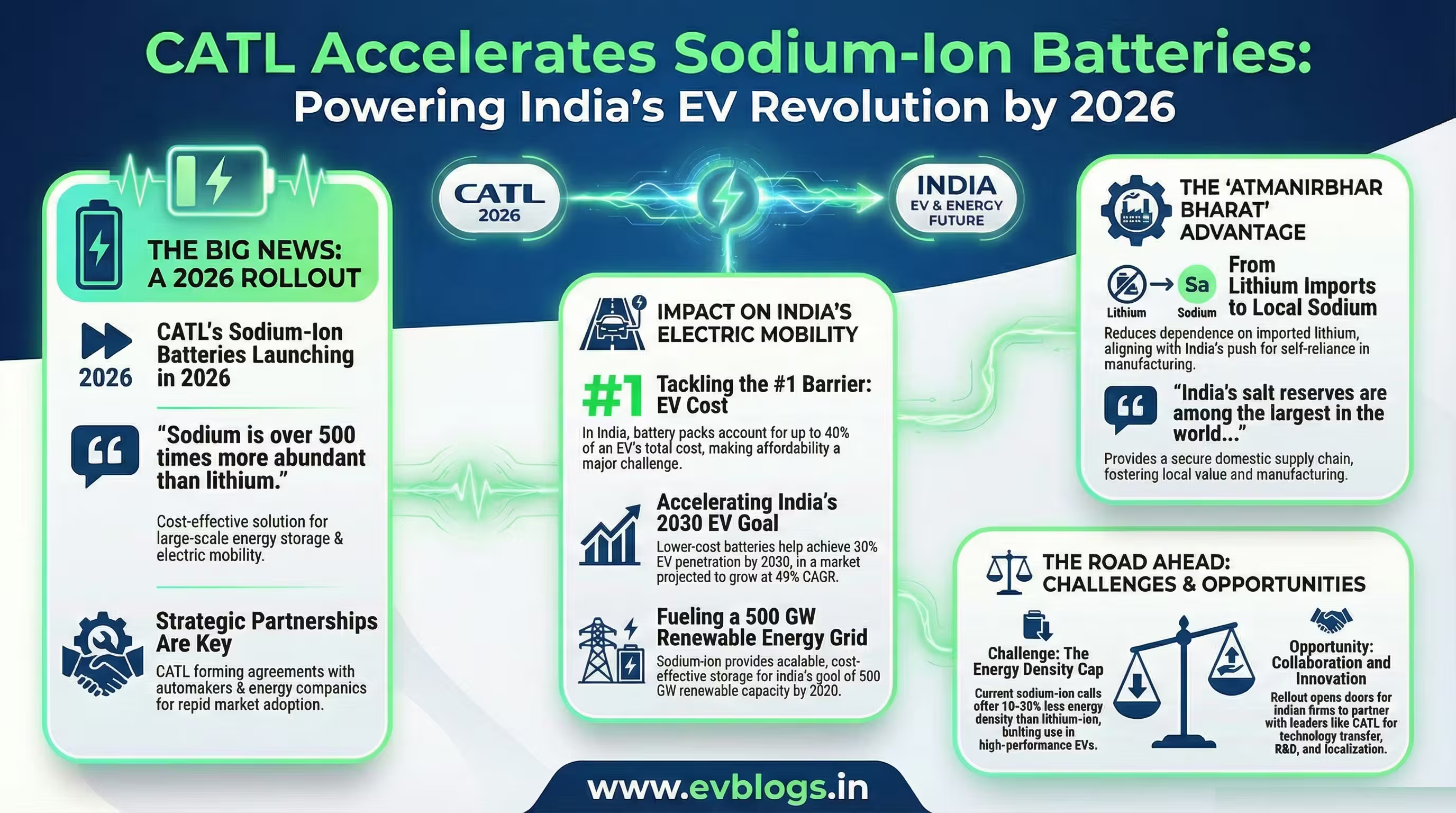
NEW DELHI, Jan 1 — Chinese battery giant Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has announced plans to accelerate the commercial launch of its sodium-ion batteries, targeting a rollout by 2026. This move is expected to have significant implications for India’s rapidly growing electric vehicle (EV) and energy storage sectors. Here are the key points you need to know:
1. CATL’s Accelerated Timeline for Sodium-Ion Batteries
CATL, the world’s largest battery manufacturer, has brought forward the launch of its sodium-ion batteries to 2026. Sodium-ion technology is seen as a potential game-changer due to its lower cost and abundant raw material availability compared to lithium-ion batteries.
“Sodium is over 500 times more abundant than lithium, making sodium-ion batteries a cost-effective solution for large-scale energy storage and mobility.”
The company’s decision to speed up development signals confidence in the readiness of this technology for commercial applications.
2. Implications for India’s EV Market
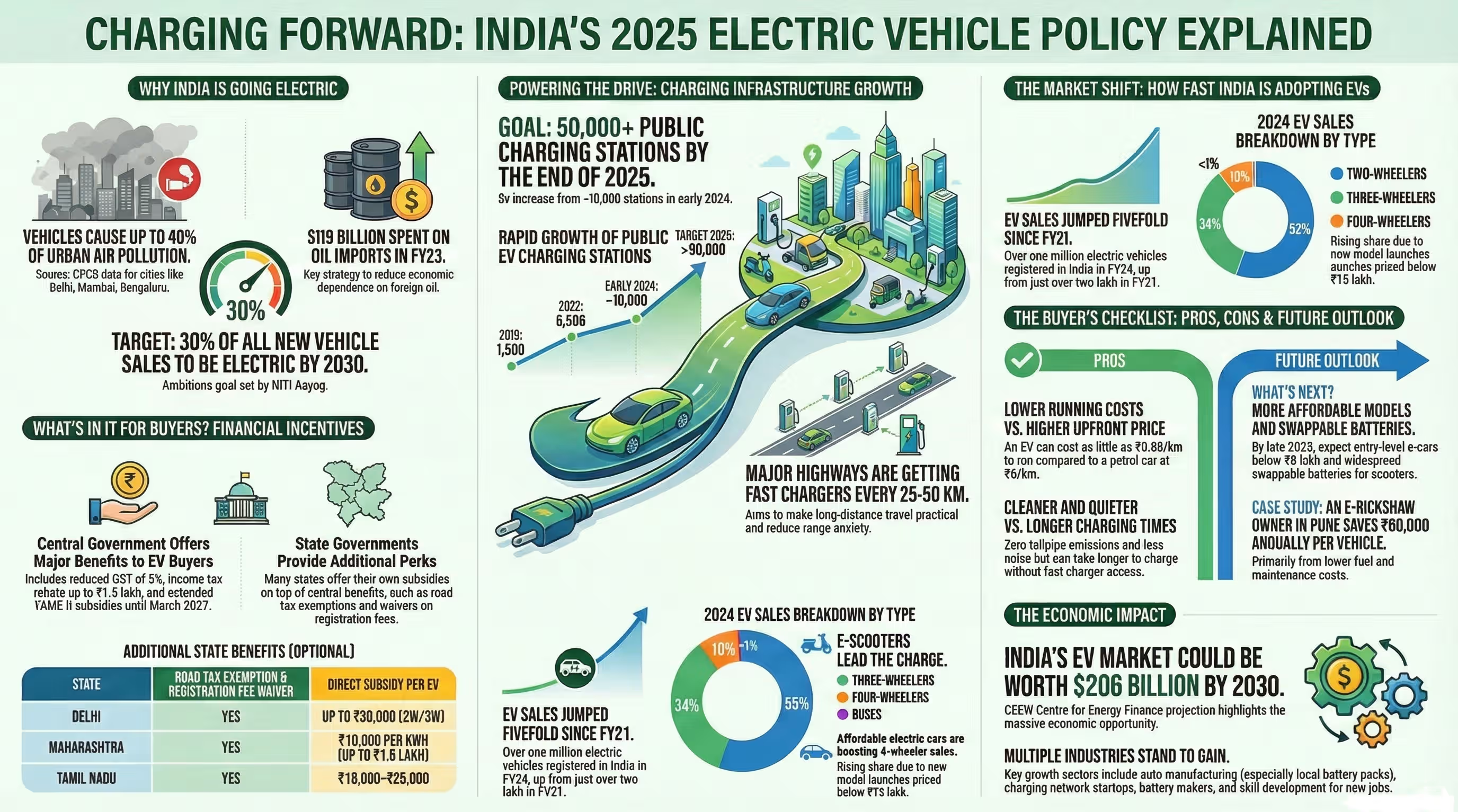
India’s EV market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 49% between 2022 and 2030, according to government estimates. Battery cost remains a critical barrier to mass EV adoption in the country.
According to NITI Aayog, battery packs account for up to 40% of an EV’s cost in India.
CATL’s sodium-ion batteries could help lower costs, making electric vehicles more affordable for Indian consumers and accelerating the government’s target of 30% EV penetration by 2030.
3. Energy Storage and Grid Stability
India’s transition to renewable energy has increased the need for efficient and cost-effective storage solutions. Sodium-ion batteries could play a pivotal role in grid balancing and renewable integration.
India aims to install 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, necessitating reliable storage solutions.
Sodium-ion technology’s scalability and lower cost could support large-scale solar and wind energy projects, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
4. Domestic Manufacturing and Raw Material Security
Unlike lithium, which is largely imported, sodium is abundantly available in India. The shift towards sodium-ion batteries aligns with India’s push for Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) in battery manufacturing.
“India’s salt reserves are among the largest in the world, providing a secure supply chain for sodium-based batteries.”
This technology could reduce dependence on lithium imports and foster local value addition through domestic cell manufacturing initiatives.
5. Potential Challenges and Considerations
While promising, sodium-ion batteries face challenges such as lower energy density compared to lithium-ion alternatives, which may limit their use in high-performance applications.
“Sodium-ion cells currently offer 10-30% less energy density than their lithium-ion counterparts.”
Continuous R&D and technological advancements will be crucial to bridge this gap and ensure sodium-ion batteries meet the diverse needs of the Indian market.
6. Opportunities for Collaboration and Innovation
The early commercialisation of sodium-ion batteries opens doors for partnerships between Indian firms and global technology leaders like CATL. Indian companies can collaborate on localisation, technology transfer, and joint research to accelerate adoption.
“Collaboration between industry and research institutions will be key to tailoring sodium-ion technology for Indian conditions.”
Such partnerships can help Indian manufacturers leapfrog to next-generation battery technologies, strengthening the country’s position in the global battery value chain.
CATL’s accelerated sodium-ion battery launch is poised to reshape India’s energy storage and electric mobility landscape. As the country strives for sustainable growth and reduced import dependence, embracing this new technology could prove pivotal in achieving national energy and climate goals.
Certainly! Here’s an additional detailed numbered point about CATL accelerating sodium-ion battery rollout for 2026, suitable for a news summary:
- Strategic Partnerships and Supply Agreements: To facilitate the large-scale deployment of sodium-ion batteries by 2026, CATL is actively forming partnerships with automakers, energy storage companies, and raw material suppliers. These collaborations aim to secure supply chains for key materials such as sodium salts and iron, streamline the integration of sodium-ion cells into electric vehicles (EVs) and grid storage systems, and accelerate commercialization. For instance, recent agreements with leading Chinese automakers and utility companies signal CATL’s intent to embed sodium-ion technology into both passenger cars and large-scale renewable energy projects, enhancing market adoption and technological maturity ahead of the 2026 rollout.
Sources
Original Source
google.com - Read original
Official Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): IPCC opens registration of experts to review the first draft of the Methodology Report on Inventories for Short-lived Climate Forcers
Quotes
- Publishing Domain: google.com
- Published Date: 2026-01-01T09:54:21+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiigFBVV95cUxQTFpTeUhMOVNnSk9UNEZJaWE2dU9tU… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 35 / 100 — The summary is almost identical to the article’s headline and source, offering minimal rewording or unique phrasing. It lacks additional context or synthesis.
- Helpfulness: 20 / 100 — The summary provides only the basic fact that CATL is accelerating sodium-ion battery rollout for 2026, without elaboration or explanation of significance, impact, or details, thus offering limited value to the reader.