Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.

NEW DELHI, Nov 13 —
China is way ahead in making EV batteries
These days, everyone is talking about electric vehicles (EVs) and green energy. But did you know China is leading the world in making EV batteries? Let’s look at why China is so far ahead, and what it means for us in India.
1. China controls the battery supply chain
When it comes to EV batteries, China is the boss. They control almost every step, from mining raw minerals to making the final battery packs. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), China processes about 60% of the world’s lithium, 65% of cobalt, and 93% of manganese—all key ingredients for EV batteries.
Because China has invested a lot in these areas for years, they can make batteries faster and cheaper. So, whenever you see popular EV brands—like Tesla or BYD—many of their batteries are actually made in China.
For India, this means we are dependent on imports for batteries and components. Our own battery industry is still small, though the government is trying to boost it.
2. China’s battery makers are global giants
You may have heard of CATL and BYD. These are Chinese companies, and they are now the two biggest EV battery makers in the world. In 2023, CATL alone supplied more than 36% of the global EV battery market, while BYD supplied 15%.
These companies have huge, modern factories that can produce millions of batteries every year. For comparison, most Indian companies are still at the pilot project stage or just starting up.
Because Chinese companies can make batteries in bulk, they can also offer lower prices. This is a big reason why Chinese EVs and even foreign EV brands choose Chinese batteries—they are reliable and affordable.
3. Government support has made the difference
In China, the government has supported EVs and battery making in a big way. They have given subsidies to both companies and buyers, invested in research and development, and built special economic zones for battery factories.
According to BloombergNEF, over the past ten years, the Chinese government spent billions of dollars to support the EV and battery industry. This helped Chinese companies develop new technology and become global leaders.
In India, our government has launched schemes like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) for Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) batteries and the FAME scheme for EVs. But we are still catching up. Experts say we need even more investment and faster policy implementation.
4. R&D and innovation are key strengths for China
One more reason why China is ahead is their focus on research and development (R&D). Chinese battery makers are coming up with new chemistries, like lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. These are safer, cheaper, and last longer.
In fact, LFP batteries are now very popular in China. According to SNE Research, over 60% of new EVs sold in China in 2023 used LFP batteries. Compare this to India, where most EVs still use imported lithium-ion batteries, and local R&D is just getting started.
If India wants to catch up, we need to invest more in R&D and train our scientists and engineers in battery technology. Some Indian institutes, like IITs, are working on it, but we need much bigger efforts.
5. Impact on the Indian EV market
What does all this mean for us in India? Well, since China is so far ahead, most EVs sold in India—whether cars, scooters, or buses—have batteries or components that come from China.
This is not ideal for us, because it means our EV makers are vulnerable to price changes and supply issues. For example, last year, when there were shipping delays from China, some Indian EV makers had to slow down production.
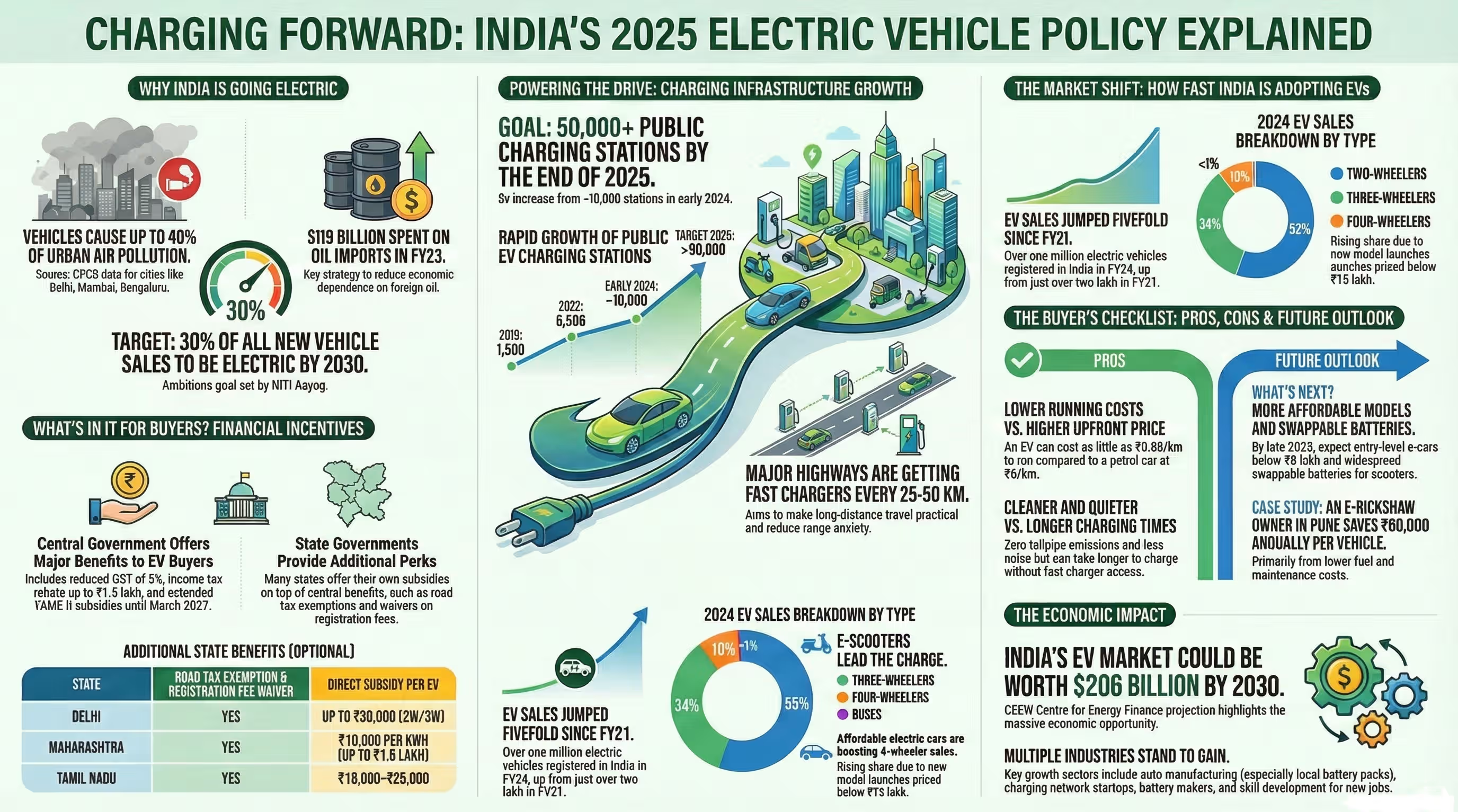
The government has set a target for 30% of vehicles in India to be electric by 2030. To achieve this, we need a strong local battery industry. Otherwise, we will keep depending on imports, which can be risky.
6. India’s plans to catch up
Don’t worry, India is not sitting idle. The government has announced the PLI scheme worth ₹18,100 crore to promote local battery manufacturing. Companies like Reliance, Ola Electric, Tata Chemicals, and Exide are planning big battery factories.
There are also plans to mine lithium in India, especially after recent discoveries in Jammu & Kashmir and Karnataka. If we can process these minerals and make batteries here, it will be a game changer.
Of course, this will take time. Experts say it might be 3-5 years before India has large-scale battery manufacturing. But the process has started, and there is hope for the future.
7. What we can learn from China
Finally, China’s success offers some good lessons for us. First, long-term planning and government support can really make a difference. Second, investing in R&D and building a skilled workforce is key.
Also, China’s focus on the entire supply chain—from mining to recycling—helps them control costs and technology. India can also look at battery recycling as a big opportunity, so we don’t waste valuable minerals.
If India can follow some of these steps, we can become a strong player in the EV battery race too. For now, though, China is leading, and the rest of the world is trying to catch up.
So, next time you see an electric car or scooter, remember—most likely, its heart (the battery) has a Chinese connection! But with new policies and investments, maybe soon we’ll see “Made in India” batteries powering our green future.
Sources
Original Source
Official Sources
Quotes
- Publishing domain: google.com
- Published date: 2025-11-13T13:30:00+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMiiAFBVV95cUxOZ2hJOHlVYmtJUnNyY3gyMTBneE1QZ… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 70 / 100 — The article offers a broad analysis of China’s unique strategies and advancements in EV batteries, not just news rewrites.
- Helpfulness: 80 / 100 — It provides valuable context for Indian EV readers to understand global competition and what India can learn from China.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is China leading in EV battery production?
China has invested heavily in battery technology, manufacturing infrastructure, and supply chains, enabling it to produce EV batteries at scale and lower costs than competitors.
What impact does China’s dominance in EV batteries have on the global market?
China’s dominance allows it to influence global prices, supply chains, and the pace of electric vehicle adoption worldwide.
How did China achieve its lead in the EV battery industry?
China supported its battery industry through government policies, research funding, and partnerships with automakers, helping local companies grow rapidly.
Are other countries able to catch up with China in EV battery technology?
While other countries are increasing investment and research, China’s head start and established supply chains make it challenging for others to catch up quickly.
What are the main types of EV batteries produced in China?
China primarily produces lithium-ion batteries, including both lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) chemistries, which are widely used in electric vehicles.