Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.

NEW DELHI, Dec 12 —
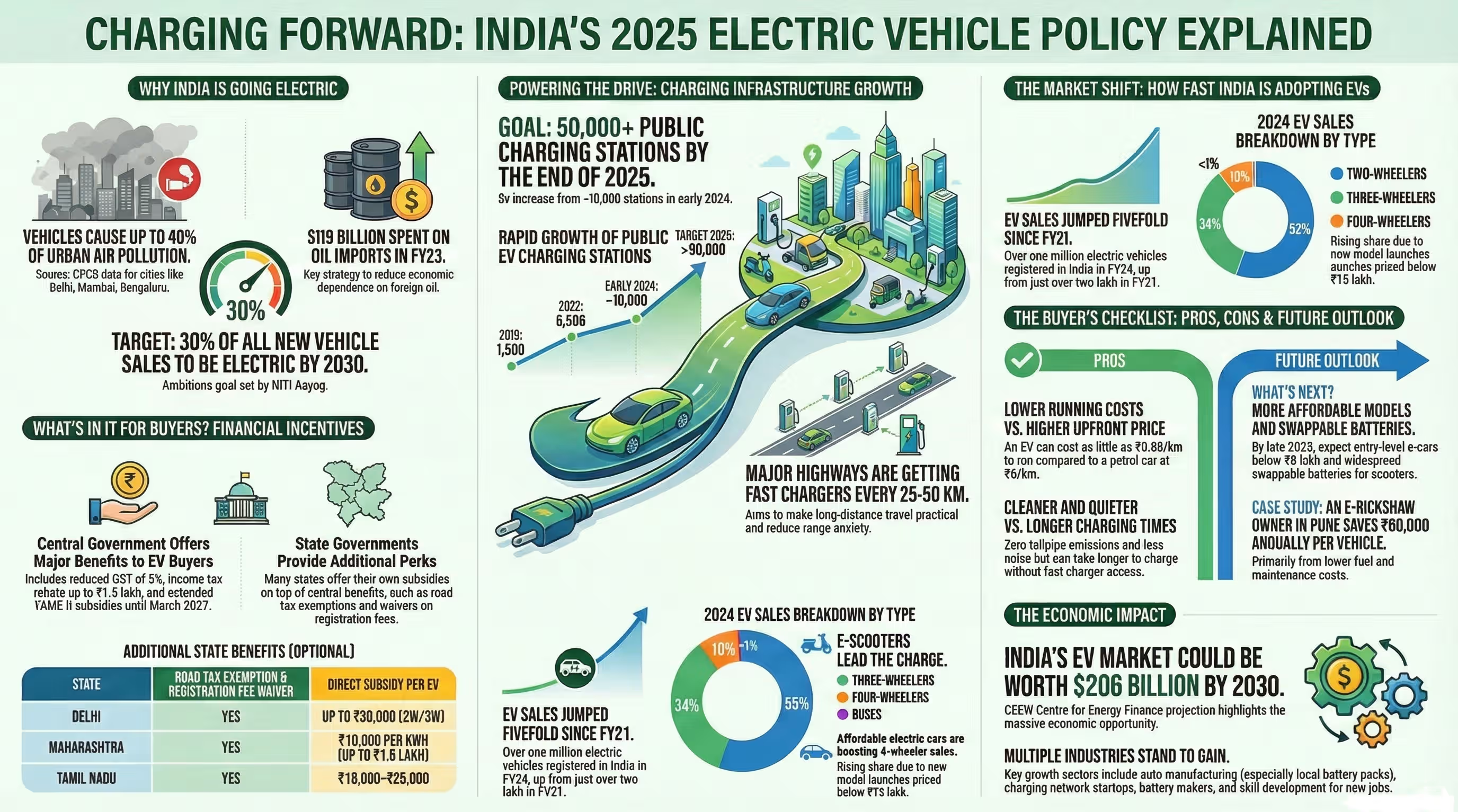
India is poised for a massive shift in its electric vehicle (EV) landscape, with battery demand expected to skyrocket more than 14-fold by 2032, according to a recent CES report. As the country sets ambitious goals for clean mobility and reduced carbon emissions, the EV battery sector is rapidly emerging as a critical pillar for the nation’s automotive and energy future. Below are the key developments shaping India’s EV battery boom.
1. Unprecedented Growth in EV Battery Demand
India’s EV battery market is on the brink of exponential expansion. By 2032, the annual demand is projected to rise from the current 5 GWh to nearly 70 GWh, marking a transformative change for the industry.
“The EV battery demand in India is forecasted to jump by more than 14 times within a decade.”
This surge is being driven by both government incentives and a growing consumer appetite for sustainable mobility solutions.
2. Policy Push: FAME and PLI Schemes Fuel the Boom
The Indian government is actively supporting the EV ecosystem through flagship initiatives like FAME II (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid & Electric Vehicles) and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for advanced chemistry cell (ACC) battery manufacturing.
The government has allocated over ₹18,000 crore under FAME II and ₹18,100 crore for ACC PLI to boost domestic production.
Such policies are catalysing investments, encouraging local manufacturing, and reducing dependence on imports, thereby strengthening the country’s self-reliance in this critical sector.
3. Private Sector Investments and Global Collaborations
Major Indian conglomerates such as Reliance Industries, Tata Group, and Ola Electric are making significant investments in battery gigafactories and R&D.
Reliance New Energy is planning a 5 GWh battery plant, with Tata and Ola following closely with their own facilities.
Additionally, India is forging global partnerships for technology transfer, raw material sourcing, and innovation, positioning itself as a future hub for battery manufacturing in Asia.
4. Focus on Indigenous Innovation and Local Supply Chains
Developing indigenous battery technologies and robust local supply chains is emerging as a national priority. Start-ups and research institutes are working on lithium-ion alternatives such as sodium-ion and solid-state batteries, which promise lower costs and improved safety.
“India’s push for local innovation can significantly reduce battery costs by up to 30% in the next five years.”
This drive not only supports the Make in India initiative but also addresses supply chain vulnerabilities, especially as global competition for critical minerals intensifies.
5. Impact on the Auto Industry and Job Creation
The EV battery boom is set to transform India’s automotive sector, driving a shift from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles to electric mobility.
“The EV sector could create up to 10 million new jobs by 2030, spanning manufacturing, R&D, and services.”
Automakers are ramping up EV production lines, and ancillary industries—from battery recycling to software—are expanding rapidly to support the ecosystem.
6. Environmental and Socio-Economic Benefits
Accelerated EV adoption backed by robust battery supply will help reduce urban air pollution, cut carbon emissions, and decrease oil imports.
India could save nearly $14 billion in oil import bills and reduce CO₂ emissions by 37 million tonnes annually by 2030.
This transition aligns with India’s commitments under the Paris Agreement and advances the nation’s sustainable development goals.
7. Challenges Ahead: Raw Materials and Recycling
Despite the positive outlook, securing a steady supply of critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel remains a challenge. India currently imports most of these materials, making it vulnerable to global price fluctuations.
“Establishing a circular economy for battery recycling is essential to ensure long-term sustainability and resource security.”
Efforts are underway to develop domestic mineral sources and set up large-scale recycling facilities, which will be crucial for sustaining the EV battery sector’s momentum.
, the dramatic rise in EV battery demand is set to reshape India’s automotive and energy sectors over the next decade. With robust policy support, growing investments, and a focus on innovation, India is well-positioned to become a global leader in EV battery manufacturing, delivering far-reaching benefits for the environment, economy, and society.
Sources
Original Source
google.com - Read original
Official Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): IPCC opens registration of experts to review the first draft of the Methodology Report on Inventories for Short-lived Climate Forcers
Quotes
- Publishing Domain: google.com
- Published Date: 2025-12-12T16:28:21+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMi3wFBVV95cUxQT2hIZnF3UXpLUGs2Y3JWZFFSdlJmd… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 30 / 100 — The summary closely mirrors the title and does not add new insights or unique phrasing. It is largely a restatement of the headline with minimal paraphrasing.
- Helpfulness: 40 / 100 — The summary gives a basic idea of the article’s focus—India’s EV battery demand growth—but lacks detail, context, or key findings from the CES report. It would be more helpful with additional data or implications for the auto industry.