Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.
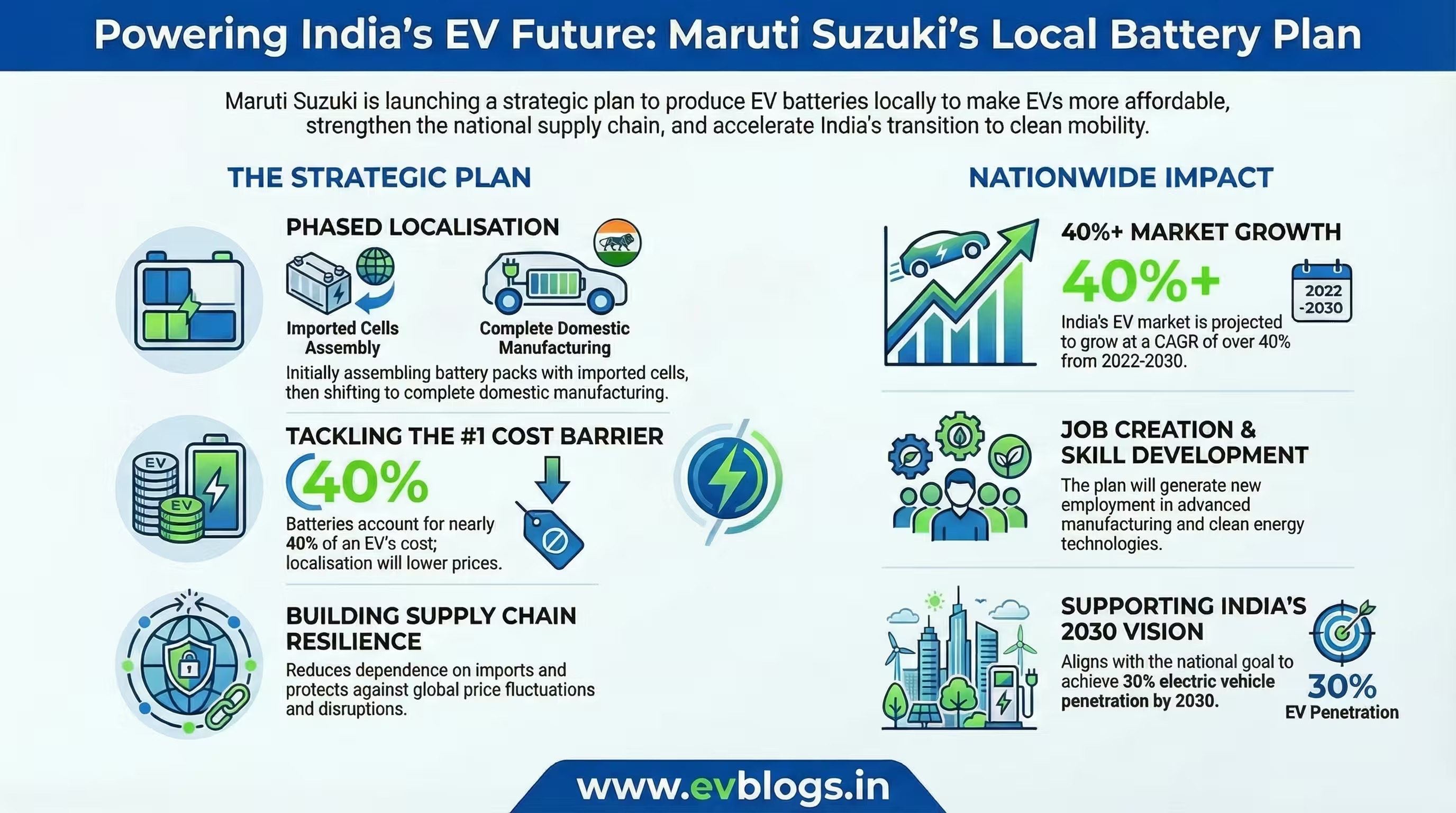
NEW DELHI, Dec 15 — Maruti Suzuki, India’s largest carmaker, is set to accelerate its electric vehicle (EV) ambitions with a focus on localising EV battery production prior to the much-awaited launch of the e-Vitara. This strategic move is expected to strengthen the company’s competitive edge and support the broader adoption of EVs in the Indian market. Below are the key aspects of Maruti Suzuki’s plan:
1. Phased Localisation of EV Batteries
Maruti Suzuki is adopting a phased localisation strategy for EV battery production. Initially, the company plans to assemble battery packs locally using imported cells, before gradually ramping up to complete manufacturing within India.
“Localising battery production is crucial to reduce costs and make EVs more accessible to Indian consumers.”
This approach is anticipated to significantly reduce the cost of EVs, which is a major barrier to adoption in the price-sensitive Indian market.
2. Strengthening India’s EV Ecosystem
The company’s decision to localise battery production will bolster India’s EV ecosystem. By developing a domestic supply chain for critical components such as batteries, Maruti Suzuki is expected to encourage investments in allied sectors like battery materials and recycling.
India’s EV market is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 40% between 2022 and 2030, according to industry estimates.
This initiative aligns with the Government of India’s vision to make the country a global manufacturing hub for electric vehicles.
3. Boosting Affordability of Electric Vehicles
One of the main challenges for EV adoption in India is the high upfront cost. Battery packs account for nearly 40% of an EV’s total cost. By localising production, Maruti Suzuki aims to reduce the price of its electric vehicles, making them more affordable to a larger section of Indian consumers.
“Affordable EVs could help accelerate mass adoption and support India’s clean mobility goals.”
The e-Vitara is expected to be competitively priced to attract both urban and semi-urban buyers.
4. Job Creation and Skill Development
Setting up battery manufacturing units is poised to generate employment opportunities and foster skill development in advanced manufacturing and clean energy technologies across India.
The auto sector currently employs over 37 million people in India, with the EV segment expected to add thousands of new jobs in the coming years.
Maruti Suzuki’s localisation efforts could contribute significantly to this employment surge, particularly in states such as Gujarat and Haryana where the company has a strong manufacturing presence.
5. Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
India’s heavy reliance on imported battery cells exposes automakers to global supply chain disruptions. By localising battery production, Maruti Suzuki aims to strengthen its supply chain resilience, ensuring steady availability of key components.
“A robust local supply chain will help mitigate risks from international price fluctuations and logistics challenges.”
This move could also inspire other automakers to follow suit, further strengthening India’s self-reliance in the EV sector.
6. Supporting India’s Sustainability Goals
Localised battery production is a vital step towards reducing the carbon footprint associated with EV manufacturing. By minimising imports and promoting domestic manufacturing, Maruti Suzuki will help decrease emissions from transportation and logistics.
India targets 30% electric vehicle penetration by 2030 as part of its commitment to climate action.
The company’s initiatives are in line with national sustainability goals and ongoing efforts to combat air pollution in major Indian cities.
Maruti Suzuki’s plan to localise EV battery production ahead of the e-Vitara launch marks a significant milestone for both the company and the Indian automotive industry. By focusing on cost reduction, supply chain resilience, and ecosystem development, the automaker is set to play a pivotal role in India’s transition to clean mobility and sustainable manufacturing.
Sources
Original Source
google.com - Read original
Official Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): IPCC opens registration of experts to review the first draft of the Methodology Report on Inventories for Short-lived Climate Forcers
Quotes
- Publishing Domain: google.com
- Published Date: 2025-12-15T13:12:06+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMi2AFBVV95cUxPOXREWndWa1hqTzQ4c3ZiMkdxc3Fme… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 30 / 100 — The summary is almost identical to the article title and does not provide additional context or unique phrasing. It simply repeats the headline with minimal modification.
- Helpfulness: 25 / 100 — The summary offers very little information beyond what is already in the title. It does not elaborate on what ‘phased localisation’ entails, the timeline, or the significance for Maruti Suzuki or the market.