Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.
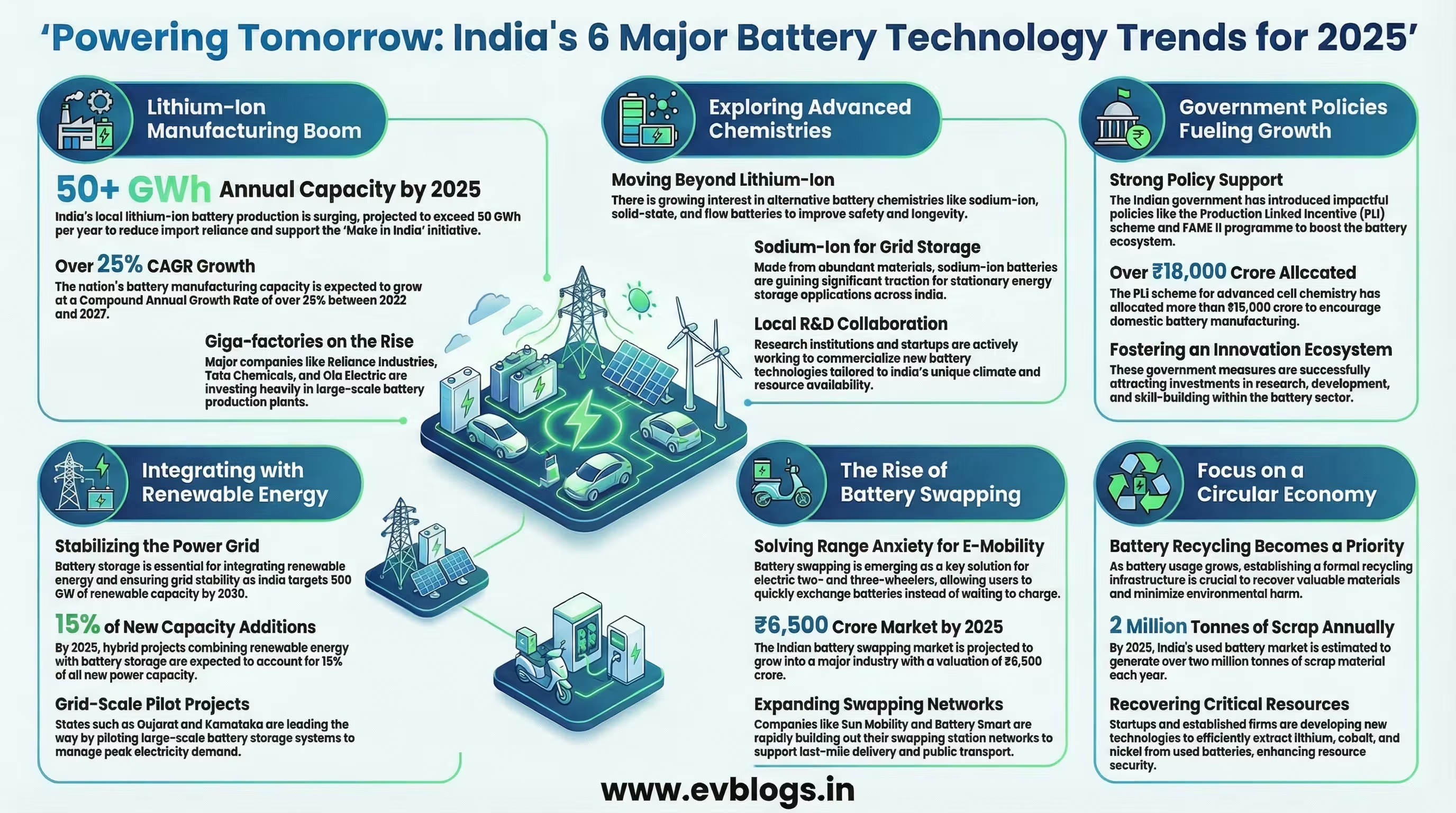
NEW DELHI, Dec 17 — As India’s energy transition gathers pace, the evolution of battery technology is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the nation’s future. With the government’s ambitious targets for renewable energy, electric mobility, and grid resilience, advances in battery innovation are critical for meeting energy demands sustainably. Here are six major battery technology trends set to define India’s energy sector in 2025.
1. Rapid Growth in Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturing
India is witnessing a significant surge in lithium-ion battery production, driven by the government’s push for electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage. By 2025, it is projected that local manufacturing capacity will exceed 50 GWh per annum, reducing reliance on imports and supporting the ‘Make in India’ initiative.
“India’s battery manufacturing capacity is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 25% between 2022 and 2027.”
Major players such as Reliance Industries, Tata Chemicals, and Ola Electric are investing heavily in giga-factories, positioning India as a global hub for advanced battery production.
2. Adoption of Advanced Chemistries Beyond Lithium-Ion
While lithium-ion remains dominant, there is growing interest in alternative battery chemistries such as sodium-ion, solid-state, and flow batteries. These technologies promise improved safety, longer life cycles, and reduced dependence on critical minerals.
“Sodium-ion batteries, which use abundant materials, are gaining traction for stationary storage applications in India.”
Research institutions and start-ups are actively collaborating to commercialise these new chemistries, aiming to address India’s unique climatic and resource challenges.
3. Integration of Battery Storage with Renewable Energy
India’s ambitious target of achieving 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 necessitates large-scale energy storage solutions. Batteries are increasingly being integrated with solar and wind projects to enhance grid stability and reliability.
“Hybrid renewable-battery projects are expected to account for 15% of new capacity additions by 2025.”
States like Gujarat and Karnataka are piloting grid-scale battery storage to manage peak demand and reduce curtailment of renewable energy.
4. Expansion of Battery Swapping Infrastructure for E-Mobility
To overcome range anxiety and charging bottlenecks, battery swapping is emerging as a key enabler for the growth of electric two- and three-wheelers in urban India. This model allows users to quickly exchange depleted batteries for fully charged ones at dedicated stations.
“The Indian battery swapping market is projected to reach ₹6,500 crore by 2025.”
Companies like Sun Mobility and Battery Smart are rapidly expanding their networks, making electric mobility more accessible and convenient for last-mile delivery and public transport sectors.
5. Government Policies and Incentives Driving Innovation
The Indian government has introduced a range of policy interventions to boost battery technology, including the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for advanced cell chemistry and the FAME II programme for e-mobility adoption.
“Over ₹18,000 crore has been allocated to support domestic battery manufacturing under the PLI scheme.”
These measures are catalysing investments in R&D, localisation, and skill development, fostering a robust ecosystem for battery innovation.
6. Focus on Battery Recycling and Circular Economy
With the expected rise in battery usage, safe and efficient battery recycling has become a priority. Efforts are underway to establish formal recycling infrastructure, recover valuable materials, and minimise environmental impact.
“India’s used battery market is estimated to generate over 2 million tonnes of scrap annually by 2025.”
Start-ups and established firms are developing recycling technologies to extract lithium, cobalt, and nickel, supporting sustainability and resource security.
India’s energy future is inextricably linked to the evolution of battery technology. As these trends gather momentum, they promise not only to support the country’s clean energy goals but also to unlock new opportunities for economic growth, innovation, and environmental stewardship.
Sources
Original Source
google.com - Read original
Official Sources
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): IPCC opens registration of experts to review the first draft of the Methodology Report on Inventories for Short-lived Climate Forcers
Quotes
- Publishing Domain: google.com
- Published Date: 2025-12-17T14:07:33+05:30
- Original URL: Read original (news.google.com/rss/articles/CBMinwFBVV95cUxPYm0zZ1lUMTFQMm1pZFJvNXh5dG1ZQ… …)
Editorial Check
- Originality: 25 / 100 — The summary is highly generic and directly mirrors the title, offering no unique perspective or additional synthesis beyond what is presented in the source headline.
- Helpfulness: 10 / 100 — The summary provides minimal information, simply repeating the title without elaborating on the six key developments or offering any context, making it unhelpful for readers seeking substantive insight.