Hedhvick Hirav
Hedhvick Hirav is a dedicated EV researcher and editor with over 4 years of experience in India’s growing electric vehicle ecosystem. Their contributions have been recognized in leading sustainability publications and automotive journals.
Summarize & analyze this article with
Choose an AI assistant and open this article directly:
Tip: if the AI doesn’t fetch the page automatically, paste the article URL manually.

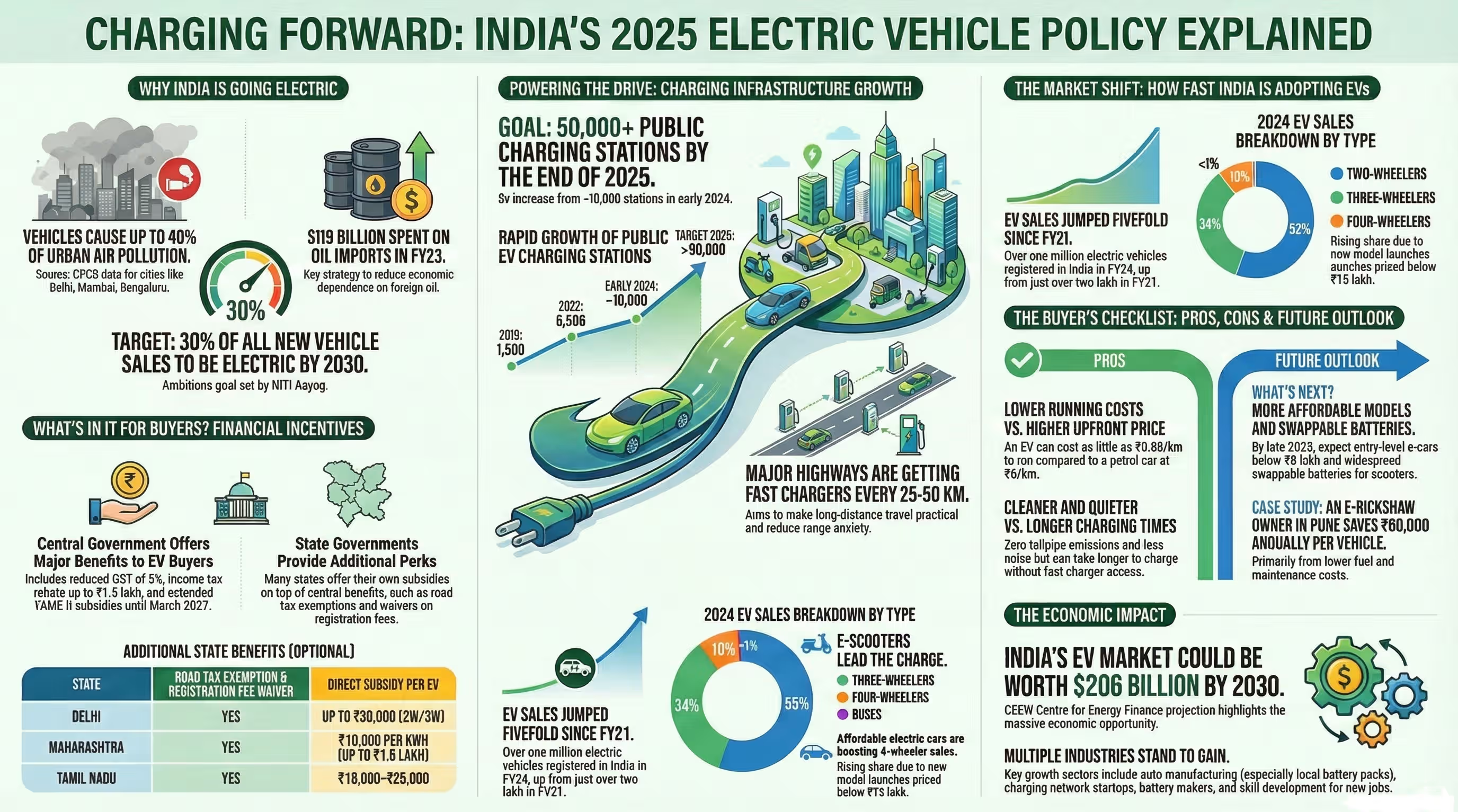
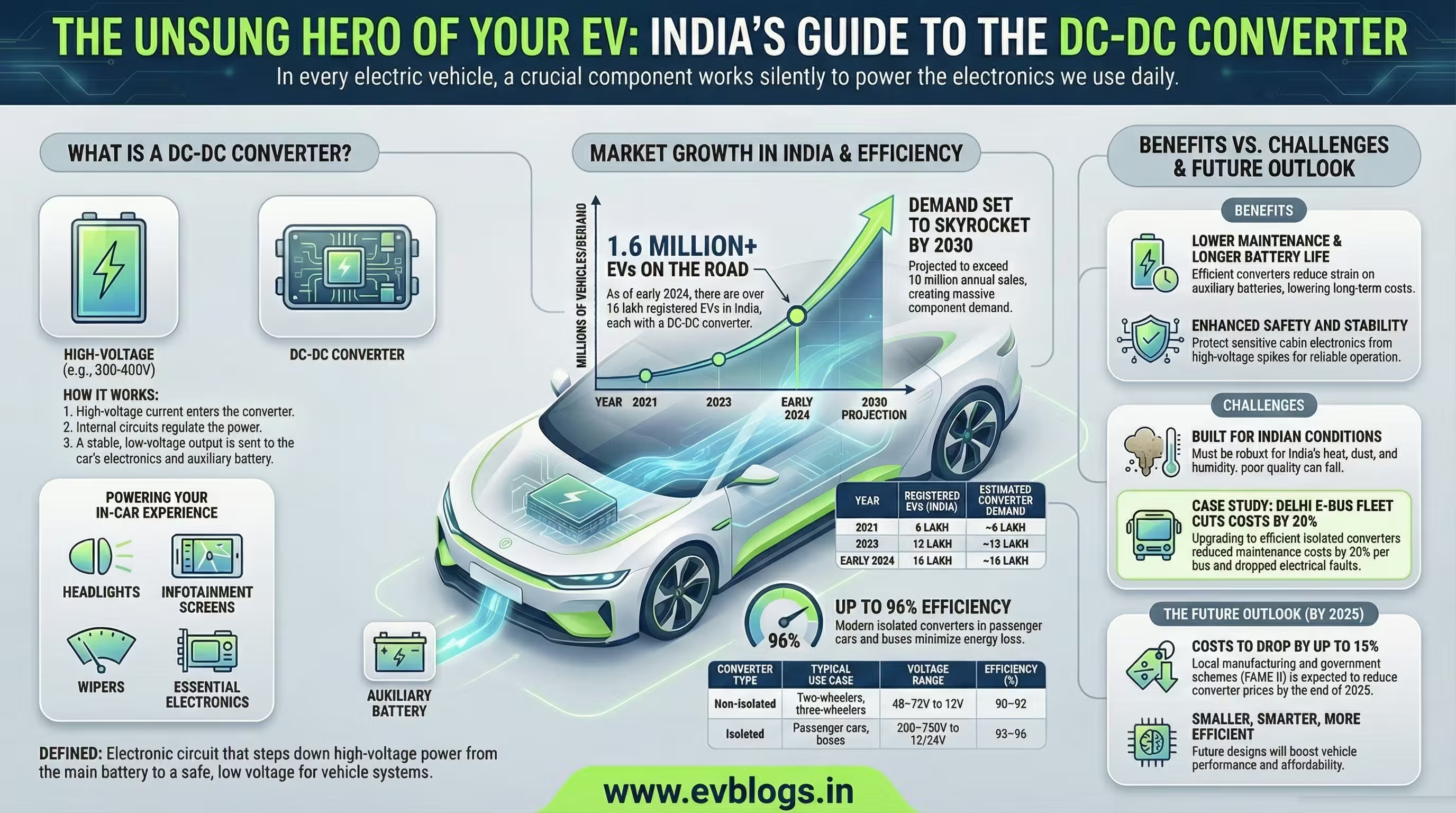
India is getting progressively electric vehicle (EV) friendly. Numerous individuals are thinking of making a switch to the electric cars but to quit the petrol or diesel cars. However one big question keeps on opening up and this is how good is the battery?
The majority of EVs in India today have lithium-ion batteries, but there is a new-fangled and superior type of battery, which makes the headlines - the Solid-State Battery.
In this blog post, we will tell all that you need to know about solid-state batteries in simple terms, including how they work, what makes them superior, who is developing them and when can we see them in India.
What is Solid-State Battery?
A solid-state battery is a rechargeable battery. It has the capacity to store energy in much the same way as your phone or laptop and electric vehicles. Nonetheless, there is a difference.
In the normal lithium-ion battery, there is a liquid or gel-like electrolyte which assists in the transfer of electric charges within the battery. In a solid-state battery, this liquid is instead solidified, but usually in ceramic, glass or some form of plastic.
This minor detail does make a significant difference in safety, the amount of energy it can hold, and the duration of time it can be used before needing to be recharged.
What makes it Different than Lithium-Ion Batteries? sky On Menlo Park, California, about 15 years ago, an inventor named Thomas Edison created a new form of battery which was quite unlike the Lithium-Ion battery.
To understand it better, we should compare the two:
| Feature | Lithium-Ion Battery | Solid-State Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte | Liquid or Gel | Solid |
| Safety | May overheat and The can be caught on fire | Much safer |
| Battery Life | 500- Question marks 1500 charge cycles | 2000+ charge cycles |
| Charging Time | Moderate (2 - 45 hrs) | Rapid ( medium-paced (15 30 mins) |
| Energy Density | Decent | Longer (More km per charge) |
| Cost (currently) | Affordable | Expensive (at least at the moment) |
As it is clear, solid-state batteries are stronger, safer and more durable. However they are still being tested in the majority of countries.
Why are Solid-State Batteries such a Big Deal in India? illes credit card claim period
India is a hot diverse country, with long distances, traffic jams and high temperatures which all impact battery performance. In India, the concern of most EV users is:
- Battery fires (overDischarge)
- Short battery life
- Sense of the loss of control (range anxiety)
- Long charging time
The solution to all these is solid state batteries. And now how:
1. the sponsored confirmation confusion range
Solid-state batteries allow more energy to be stored in a smaller area. This will enable an EV to travel 400-800km on a single charge, which is ideal in driving long distances on the Indian highways or interstate.
2. Better charging Heavier charging Charging less
Solid-state technology enables quicker charging, up to 1530 minutes to charge, about the time of filling a petrol tank.
3. Falsified (Latin)Locale (English)
There is nothing flammable inside it, which eliminates battery fires and explosions even in the Indian summer.
4. Greater battery power
You will no longer need to change the battery after every couple of years. With such batteries, it is easy to have them last more than 10 years hence making EVs more cost effective in the long run.
Which companies are the world leaders in developing solid-state batteries?
There are numerous international companies that are investing a lot into the research of solid-state batteries. The best of the best include:
Toyota (Japan) uses the argument that the online selling of the product is not a patent infringement.
Toyota is among the earliest companies to invent solid-state batteries. Their first pure solid state EV is scheduled release in the 20272028 time frame. Their hybrid models are also very reliable and people are looking forward to their EVs performance.
QuantumScape (USA) Established 2014 Founder 1 Richland Energy Headquarter San Jose, California, United States Website quantumscape.com
This Berkeley-based American startup has been trailing solid-state batteries with interesting results, and is supported by Volkswagen. They have faster charging batteries and higher energy storage compared to the current lithium-ion batteries.
Compañía Samsung SDI (Corea)
Samsung does not only produce phones Their battery division is engaged in the development of advanced solid-state cells that have superior safety and performance.
The Mustard Wake-up (v.est.8) (Usa) - Mustard Wake-up (v.est.8)
Ford and BMW support Solid Power, which designs and manufactures prototype batteries and plans to start commercial production in the coming years.
Asian-Chinese Republicans (S)-High
The giant of the lithium-ion battery industry is also investigating hybrid solid-state technology to enhance performance.
Roma (Taiwan),
This firm has been collaborating with a number of international partners and has recently signed an MoU to establish battery plants in India.
What is going on in India?
In India, it is not lagging too much behind There is a slow movement of many Indian companies entering this space and preparing themselves to gear up to the battery revolution.
Tata Group
Tata exudes confidence with cars like the Nexon EV and the Tiago EV, which presently lead in the EV market in India. Tata Chemicals is also developing high-tech battery materials, which could be used in producing solid-state batteries in future.
Ola electric is on a mission to bring safer, convenient electric two-wheeler every day by month 12.
Ola is constructing a gigafactory in Tamil Nadu, which can be manufacturing solid-state batteries in the future. They also are working on new battery technology on their electric scooters and cars in the future.
Exide and Amara Raja equipment
These are some of the largest battery manufacturers in India. Both are focusing on next-gen battery technology and can begin to manufacture solid-state batteries with partners around the world.
Materials
An Indian startup that has developed a quick-charging battery in electric vehicles and solids research using graphene and other high-tech materials.
India Government of Autonomous
India government is launching a big push to EV and battery production in the form of policies:
Away to the West a e farther to the West
FAME which can be abbreviated as Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles is a program which allows subsidies to make EVs more affordable and this promotes battery research.
This leads to the acceptance of the production-related incentive (PLI) program Just about everybody can stand to gain and this is the reason I recommend this program.
Under this, the government is also encouraging mass battery production in India, which includes recently developed technologies such as solid-state batteries.
NEMMP
This mission is making an ecosystem in which India can be a global EV and battery hub.
All these go to say that the environment is gradually becoming battery-friendly, and in a short time, there will be the support that companies need to launch solid-state batteries in the Indian market.
What are the challenges?
Solid-state batteries are the dream, but they are not quite there yet. Here are some of the issues that scholars and product designers are yet to overcome:
1. High cost eW eM b Hellac past
Current solid-state batteries are two to four times more expensive than lithium-ion batteries. However, the price will decrease as more companies manufacture them.
2. healthy foods
The production of a solid-state battery will have to be carried out with new plants, equipment, and human resources. Moving from liquid to solid technology can not be done overnight.
3. Voir {Tfin Rapport Morceau Tomberies homepage}
The solid materials to be used should be thin, strong, and efficient. Scientists are still experimenting on what material is best used
4. This has not been produced in large volumes {wp-block-heading} Ta
The majority of solid-state batteries remain in the lab or are still in a prototype phase. They might be ready to be used regularly in 2-5 years.
When will Solid-State Batteries be Available in Indian Electric Vehicles?
Most observers predict that it will take until 2027-2030 before we start seeing solid-state EVs in India.
They will initially be applied in luxury electric cars or large ones. Gradually, as manufacturing scales and price decreases, they will be utilised in entry-level EVs, scooters, and buses.
To Wait or to Buy an EV Now?
This depends on your requirements.
In case you want an EV nowadays, to use in your everyday commute, business, or ride-sharing, it is safe to buy lithium-ion-based EVs. Some of the good models and well-supported in India are the Tata Nexon EV, MG ZS EV, or Hyundai Kona EV.
But, in case you are planning on going electric in 3-5 years or so, it is certainly worth keeping a close eye on the market. Solid-state batteries have the possibility to provide your driving experience with a game-changing experience.
Long battery life
Solid-state batteries are not fantasy. They exist and several of the largest companies in the world are trying their level best to make them become part of everyday EVs.
To the Indian consumers, this may mean:
- Greater range on tires per charge
- Quicker charging
- Safer driving
- Longer battery time
- Reduced long term maintenance fees
The technology continues to develop, but has a lot of potential when it comes to electric vehicles in India. As Indian startups show increasing interest in solid-state batteries, as the government supports them, and as the world researches them, the time may not be far to reach when solid-state batteries can bring efficiency and clean power to electric vehicles on the roads.
Either way, you are an EV owner, a car buyer, or learning about new technologies, keep a close eye on solid-state battery development in India.
Thanks, reader!
If you enjoyed this post, share this with friends and family who are considering an EV purchase.